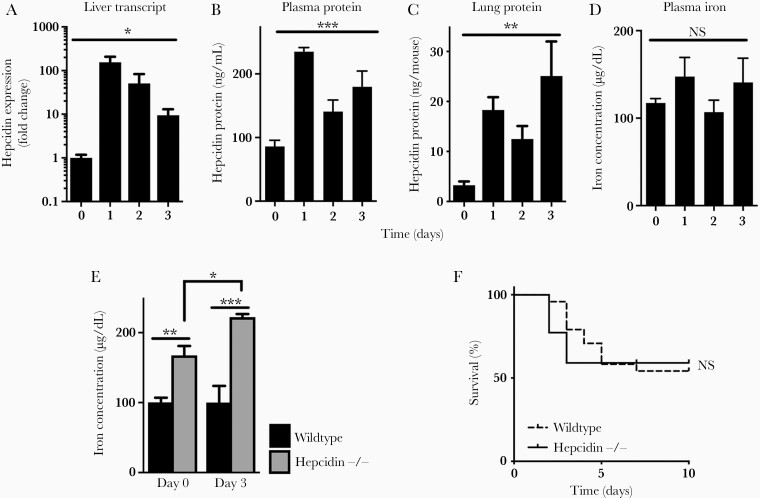
Figure 2.
Hepcidin induction and plasma iron during invasive pulmonary aspergillosis. (A) Liver hepcidin messenger ribonucleic acid in the liver normalized to glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase expression and then to day 0. (B and C) Hepcidin protein concentration in plasma and whole lung homogenate after infection. (D) Plasma iron concentration. (E) Comparison of plasma iron concentration in wild-type and hepcidin-deficient mice before and during invasive aspergillosis. (F) Survival of neutropenic wild-type and hepcidin-deficient mice during invasive aspergillosis. Time 0 represents neutropenic but uninfected animals. Data in panels A–E represent mean ± standard error of the mean of n = 3–10 animals per time point; for panel F, n = 22–24 per group, combined results of 2 experiments. *, **, and *** denote P < .05, P < .01, and P < .001, respectively. NS, no significant difference.