Figure 7.
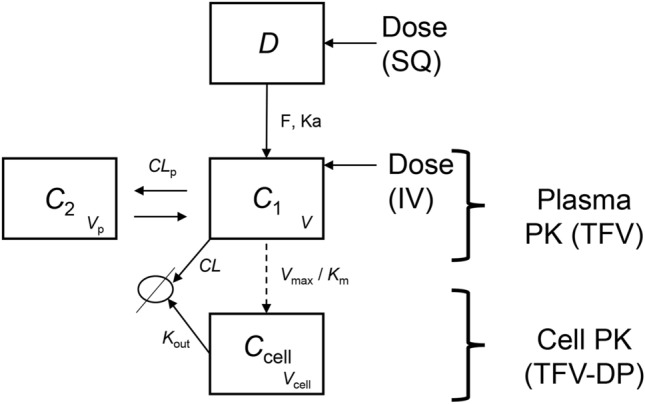
Pharmacokinetic model for plasma TFV and intracellular TFV-DP in mice, based on the model reported by Duwal et al.44. IV dosing occurs in the C1 compartment, SQ and implant dosing occur in the D compartment (dosing reservoir). The release rate into the D compartment is assumed instantaneous following SQ dosing, but is governed by the actual implant TAF release rate in the case of implant administration. The fraction of TAF metabolized to TFV is assumed to be 100%. V, volume of distribution of the central compartment; CL, total body clearance; Vp, volume of distribution of the second compartment; CLp, clearance from the second compartment; t1/2, elimination half-life; F, bioavailability/exposure scaling; Ka, absorption rate parameter; Vcell, PBMC physiological volume; Kout, elimination rate parameter; Vm, maximum rate achieved by the system using Michaelis–Menten kinetics; Km, Michaelis constant.
