Figure 1.
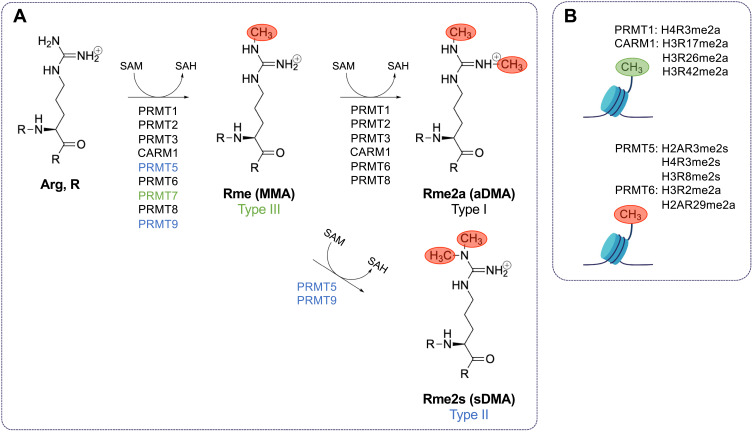
Type I, II, and III PRMTs mediate the methylation of arginine using S-adenosyl-methionine. (A) Type I protein arginine (Arg, R) methyltransferases (PRMTs) (PRMT1, PRMT2, PRMT3, CARM1, PRMT6, and PRMT8) catalyze the formation of monomethylarginine (Rme1, MMA) and asymmetric dimethylarginine (Rme2a, aDMA) by transferring methyl groups from S-adenosylmethionine (SAM) to the ω-guanidino nitrogen atoms of arginines in proteins. S-adenosylhomocysteine (SAH) is produced in each methyltransferase reaction. Type II PRMTs (PRMT5 and PRMT9) catalyze the formation of MMA and symmetric dimethylarginine (Rme2s, sDMA). PRMT7 is the only known type III PRMT, and it catalyzes the formation of only MMA. There are currently no known dedicated arginine demethylases. (B) PRMT1-catalyzed H4R3me2a and CARM1-catalyzed H3R17me2a, H3R26me2a, and H3R42me2a, and PRMT5 H3R2me2s are activating histone marks, while PRMT5-catalyzed H2AR3me2s, H4R3me2s, and H3R8me2s; PRMT6-catalyzed H3R2me2a; and CARM1-catalyzed H2AR29me2a are repressive histone marks.