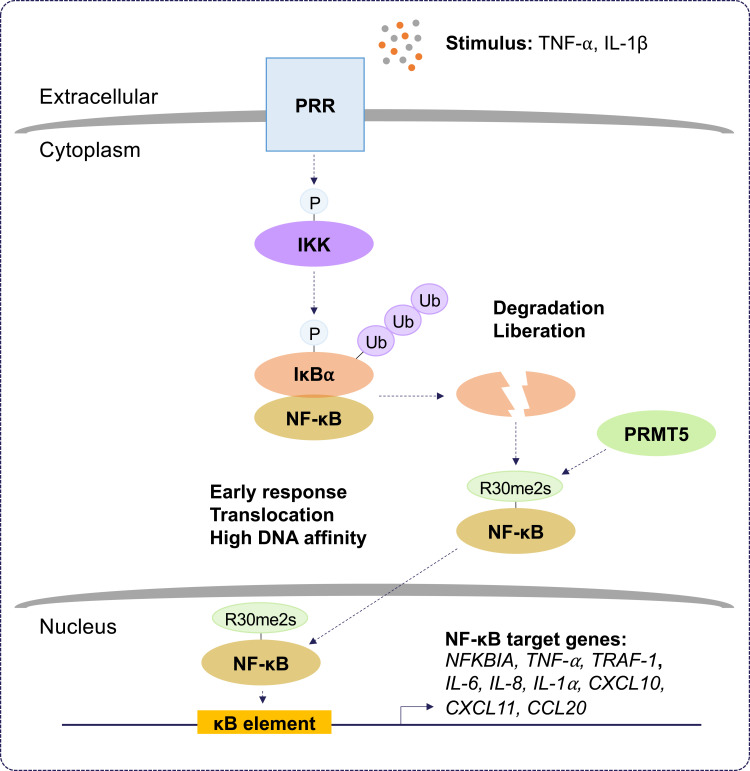
Figure 3.
The role of PRMT5 during inflammation. Protein arginine methyltransferase 5 (PRMT5) positively regulates the nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) pathway. Pattern recognition receptor (PRR) stimulation by tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) and interleukin-1 beta (IL-1β) results in the activation of inhibitor of kappa B (IκB) kinase (IKK). IKK activation leads to proteasomal degradation of IκB alpha (IκBα). This liberates NF-κB and allows PRMT5 to symmetrically dimethylate (Rme2s) the NF-κB subunit, RelA/p65, at R30. Symmetric dimethylation of NF-κB increases its affinity for kappa B (κB) sites with the consensus sequence 5’-GGGRNYYYCC-3’, where R is an unspecified purine, Y is an unspecified pyrimidine, and N is any nucleotide, and this supports the activation of promoters regulating NF-κB target genes. Symmetric dimethylation of NF-κB is postulated to function as an early response in NF-κB activation.