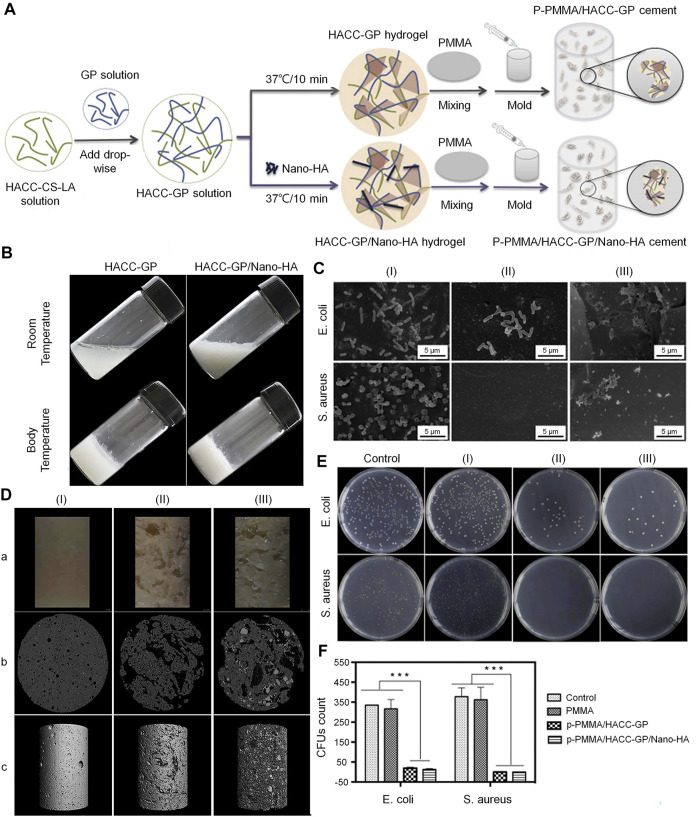
FIGURE 1.
Incorporation of PMMA cement into a HACC-based hydrogel to form a new composite system with dual function for the treatment of infected bone defects (Wang et al., 2018b). (A) Synthesis of PMMA-based cement. (B) Morphological external phase of HACC-GP and HACC-GP/Nano-HA hydrogel at room temperature and body temperature. (C) Bacteriostatic results based on scanning electron microscopy (SEM). (D) Surface morphologies (a) and μ-CT observations (b, c) of PMMA-based cements. (E,F) Agar plate diffusion and colony count results of PMMA-based cements against E. coli and S. aureus. CFU, colony forming unit; CS, chitosan; E. coli, Escherichia coli; GP, glycerophosphate; HA, hydroxyapatite; HACC, N-(2-hydroxyl)propyl-3-trimethylammonium chitosan chloride; LA, lactic acid; μ-CT, micro-computed tomography; PMMA, polymethylmethacrylate; S. aureus, Staphylococcus aureus.