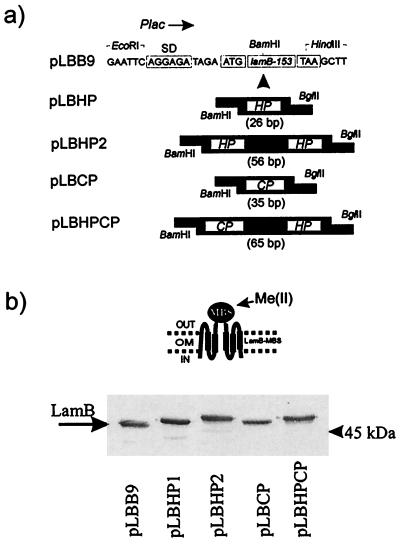
FIG. 2.
(a) Organization of the lamB-mbs gene within the pLBB9 expression vector (a derivative of the low-copy-number vector pVDL8 bearing lamB-153 gene expressed throughout the lac promoter). The orientation of the promoter is marked by an arrow. The ribosome binding site (SD), the initiation codon (ATG), and the stop codon (TAA) of lamB-153 are indicated. The plasmids relevant to the specific genetic insertions of mbs indicated are listed on the left. For the amino acid compositions of the MBSs see Table 1. (b) Expression of LamB-MBD in E. coli pop6510. Crude extracts of approximately 2 × 108 cells of E. coli pop6510 expressing LamB variants were resolved by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, probed with preadsorbed polyclonal rabbit anti-LamB serum, and visualized with goat anti-rabbit antibody conjugated with alkaline phosphatase. The arrow indicates the position of wild-type LamB protein. The drawing shows the desired targeting of LamB-MBSs into the OM of E. coli. The LamB protein consists of 18 transmembrane domains, and the MBSs are introduced between transmembrane domains 7 and 8 of the protein.