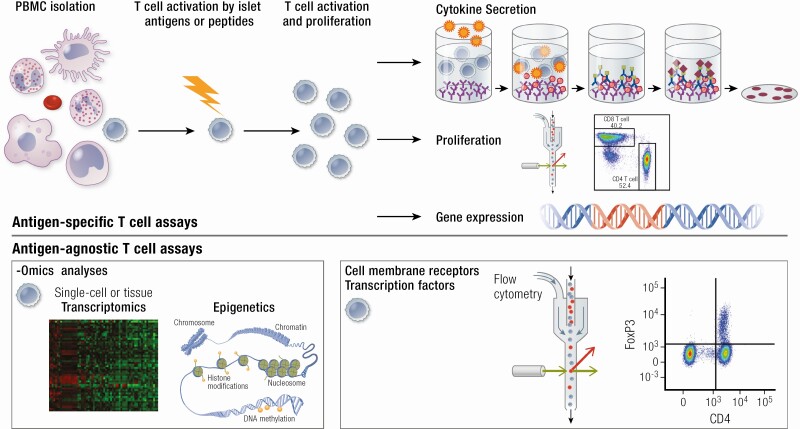
Figure 3.
Antigen-specific and antigen-agnostic T cell phenotyping. Antigen-specific T cells are profiled following incubation with islet autoantigens or peptides such as preproinsulin or neoepitopes. Activated T cell populations can be characterized through quantification of cytokine secretion, proliferation, and gene expression. Antigen-agnostic T cells are not first activated by islet autoantigens. Bulk- and single-cell -omics analyses have improved T cell transcriptional and epigenetic characterization. Flow cytometry is used to phenotype T cells based on cytokine expression and cell surface markers as well as (phosphorylation of) intracellular proteins and nuclear transcription factors that are key for regulating T cell function (FoxP3 depicted here).