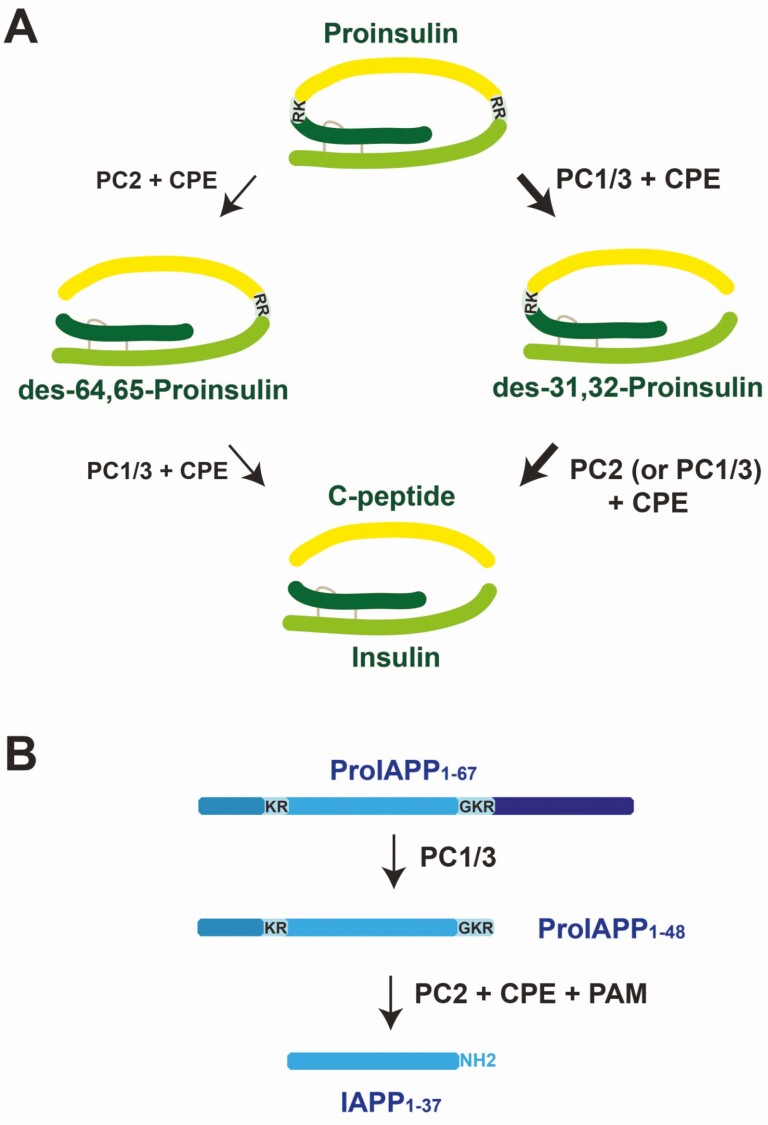
Figure 5.
Pathways for β-cell prohormone processing. A, Pathway for proinsulin processing in β cells. The predominant pathway for proinsulin processing to insulin and C-peptide involves cleavage of proinsulin by prohormone convertase (PC) 1/3 on the C-terminal side of basic residues at positions 31 and 32, followed by the removal of these basic residues by carboxypeptidase E (CPE), leading to the production of the proinsulin intermediate, des-31,32 proinsulin. This intermediate is then cleaved by PC2, or in human β cells may be cleaved by PC1/3, leading to production of one molecule of insulin and one of C-peptide. Another possible pathway involves cleavage of proinsulin by PC2 on the C-terminal side of basic residues at amino acids 64 and 65 which, following removal of these residues by CPE, is predicted to lead to des-64,65 proinsulin, although this pathway is not thought to be active in healthy β cells as the des-64,65 proinsulin intermediate is undetectable in human plasma. B, Pathway for proIAPP processing in β cells. Like proinsulin, proIAPP1-67 is first processed by PC1/3 on the C-terminal side of a pair of basic amino acids, near the C-terminus of the propeptide. Following removal of these basic residues by CPE, the N-terminally extended proIAPP intermediate proIAPP1-48 is formed. ProIAPP1-48 processing to mature IAPP is dependent on PC2 in murine β cells. Mature IAPP (and possibly proIAPP1-48) is amidated in secretory granules at the C-terminus by peptidyl α-amidating monooxygenase (PAM).