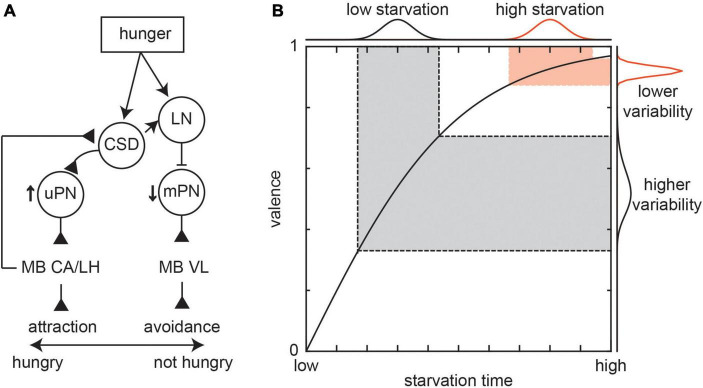
FIGURE 3.
Effect of internal states on behavioral variability. (A) Effect of hunger on larvae attraction or avoidance to geranyl acetate. When hungry, the CSD neuron potentiate attraction mediating uPN responses while LNs inhibit aversion mediating mPN responses through glutamatergic mPNs. This leads to a switch from avoidance to attraction through downstream connections to the mushroom body calyx (MB CA), mushroom body vertical lobe (MB VL), and lateral horn (LH). Figure based on Vogt et al., 2021. (B) The variability in behaviors such as attraction depends on the relationship between the behavior and internal states like hunger (represented by starvation time). In this cartoon, two groups of flies that have the same variance in starvation times, the flies that are starved more should show less variability in valence. However, experiments typically show a higher level of valence variance than that predicted by theoretical average relationship curves.