FIGURE 1.
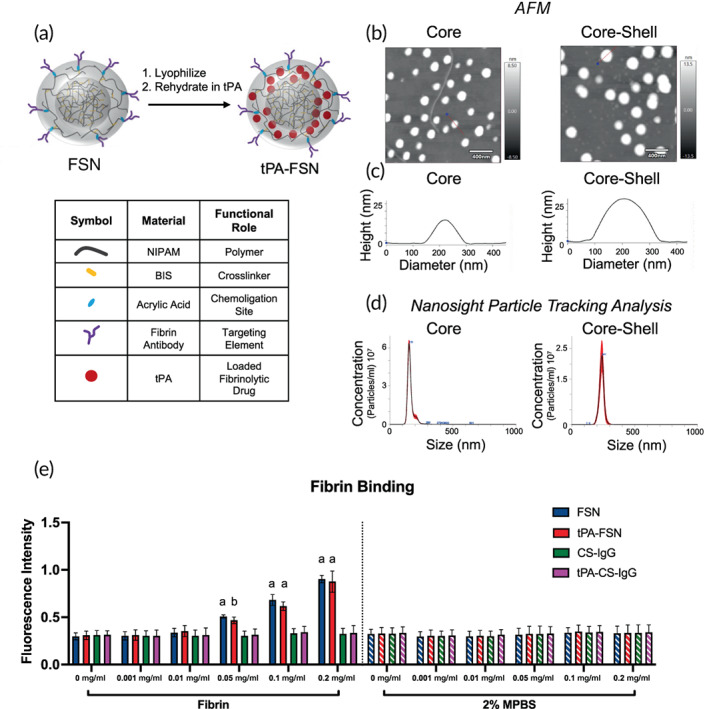
Overview of tissue‐type plasminogen activator‐fibrin‐specific nanogels (tPA‐FSN) particle design and characterization. (a) Core‐shell nanogel composition and schematic of tissue‐type plasminogen activator (tPA) loading into FSNs. (b) Representative atomic force microscopy (AFM) images of core and core‐shell nanogels. (c) Representative height traces of single particles (depicted with a red line through the center) from AFM images of core and core‐shell nanogels. (d) Particle size distribution of hydrodynamic diameter measurements from the core and core‐shell nanogels utilizing NanoSight particle tracking analysis software. At least 108 core and core‐shell nanogels were tracked. (e) Fibrin binding assay of FSNs, tPA‐FSNs, control sheep immunoglobulin G (CS‐IgG) particles, and tPA‐CS‐IgG particles at 0, 0.001, 0.01, 0.05, 0.1, and 0.2 mg/ml concentrations on fibrin‐coated wells or negative control 2% powdered milk in phosphate‐buffered saline (MPBS) wells (n = 6–9/group). Mean ± SD is shown. Data were analyzed via a two‐way analysis of variance with a Tukey's post hoc test using a 95% confidence interval. a: p < 0.0001 b: p < 0.001 compared to IgG control particle types
