FIGURE 1.
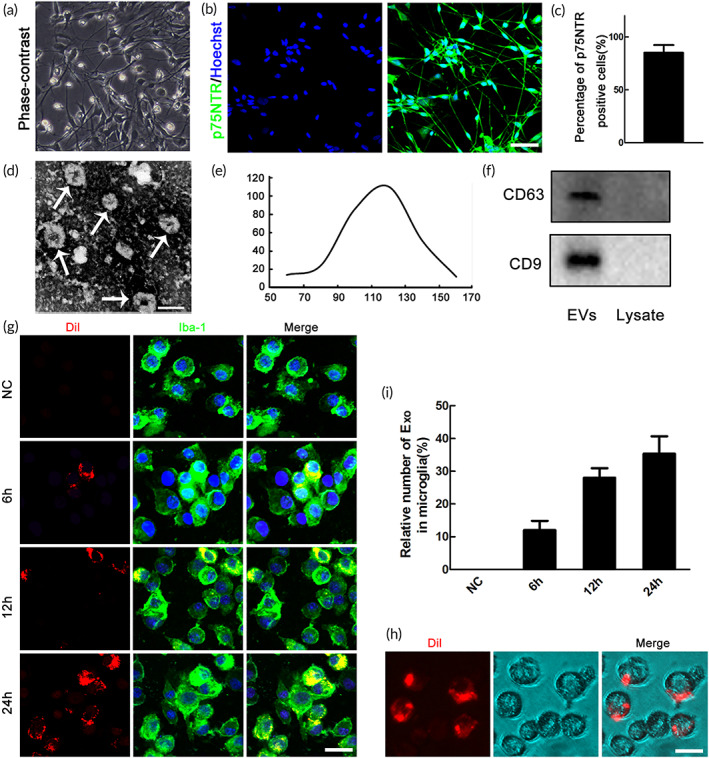
Characterization of OECs‐derived extracellular vesicles (EVs) and uptake of DiI‐labeded OECs‐Exo by microglia. (a) Identification of primary cultured olfactory ensheathing cells (OECs). Brightfield photomicrographs of olfactory ensheathing cells. (b) Immunocytochemistry of P75NTR. (c) Statistics revealed that about 90% of the purified cells were p75NTR positive. Scale bar = 50 μm. (d) Representative transmission electron microscope (TEM) image showing the morphology of OECs‐EVs. Scale bar = 120 nm. (e) Nanoparticle tracking analysis (NTA) showing the size distribution of OECs‐EVs. (f) Western blotting analysis showing the presence of EVs marker proteins of CD9, CD63 in OECs‐EVs. (g) Representative confocal microscopy images showing time‐dependent uptake of DiI‐labeded OECs‐Exo (red) by microglia (green). Note that no OECs‐Exo in negative control (NC) groups. (h) Representative images of brightfield microscopy representing DiI‐labeded OECs‐Exo (red) in microglia, and the corresponding quantification (i) of changes of relative fluorescence intensity at different time points. Scale bar = 10 μm
