Extended Data Fig. 7 |. BSL1 Physically Interacts with YDA in vitro and in vivo.
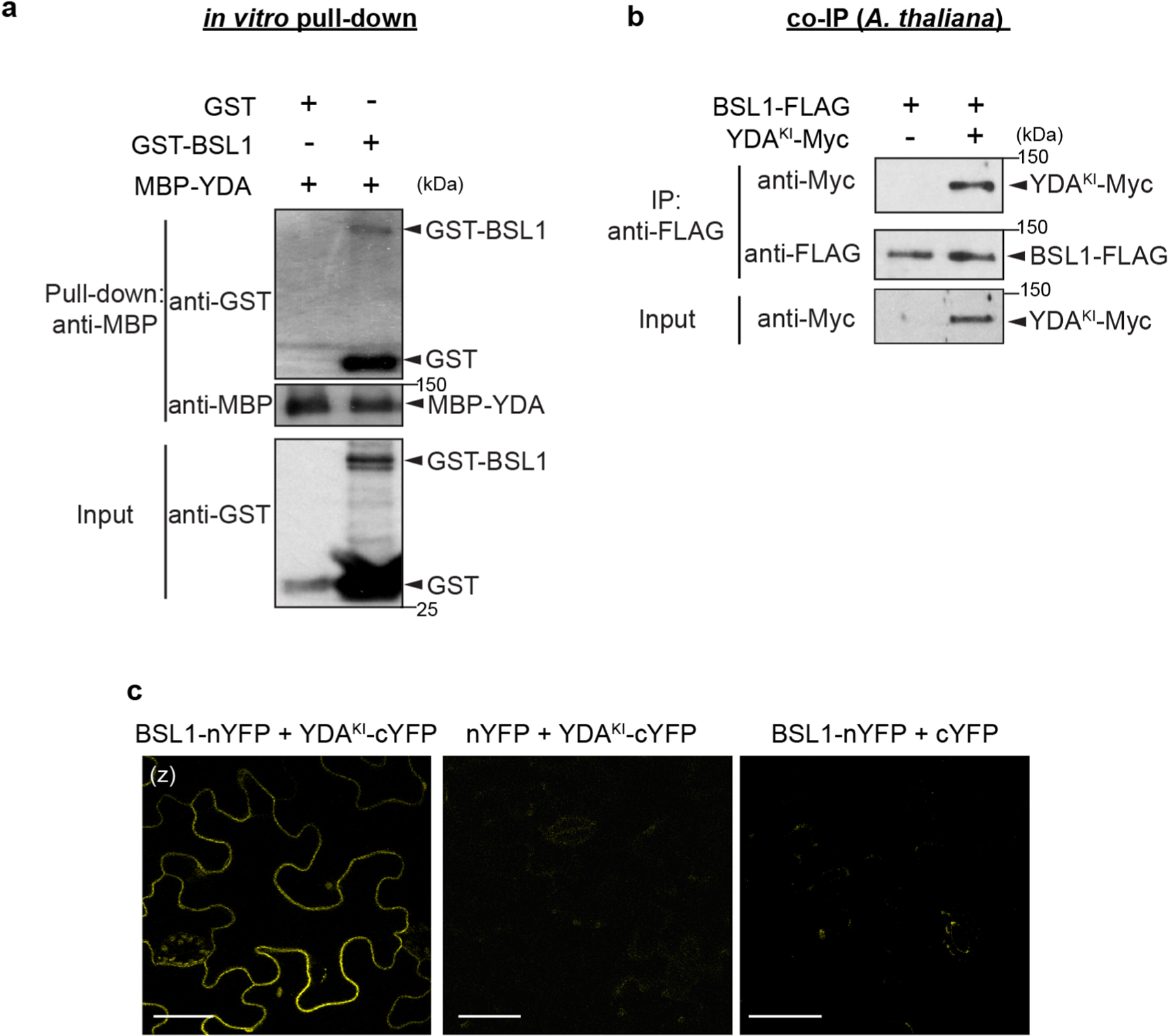
a, In vitro pull-down assays using purified recombinant proteins show GST-BSL1 interaction with MBP-YDA. MBP-YDA used as bait. GST (negative control) or GST-BSL1 interaction were detected by anti-GST. b, Co-IP data show in vivo interaction between BSL1 and YDA. BSL1-FLAG was used as bait to detect the binding of YDAKI-Myc in 5-dpg Arabidopsis seedlings. The expression of BSL1-FLAG is driven by the TMM promoter and the expression of YDA is driven by the BASL promoter. YDAKI (Kinase Inactive YDA) was used to avoid the activity of YDA strongly suppressing plant growth. Data represent results of experiments repeated three times in a and b. c, BiFC assays show the interaction between BSL1 and YDAKI (kinase inactive YDA variant used to suppress active YDA-triggered cell death) occurs at the cell membrane in N. benthamiana leaf epidermis. Positive protein-protein interactions were visualized by YFP signal (yellow). Half YFPs (nYFP or cYFP) were uses as negative controls. Scale bars, 50 μm.
