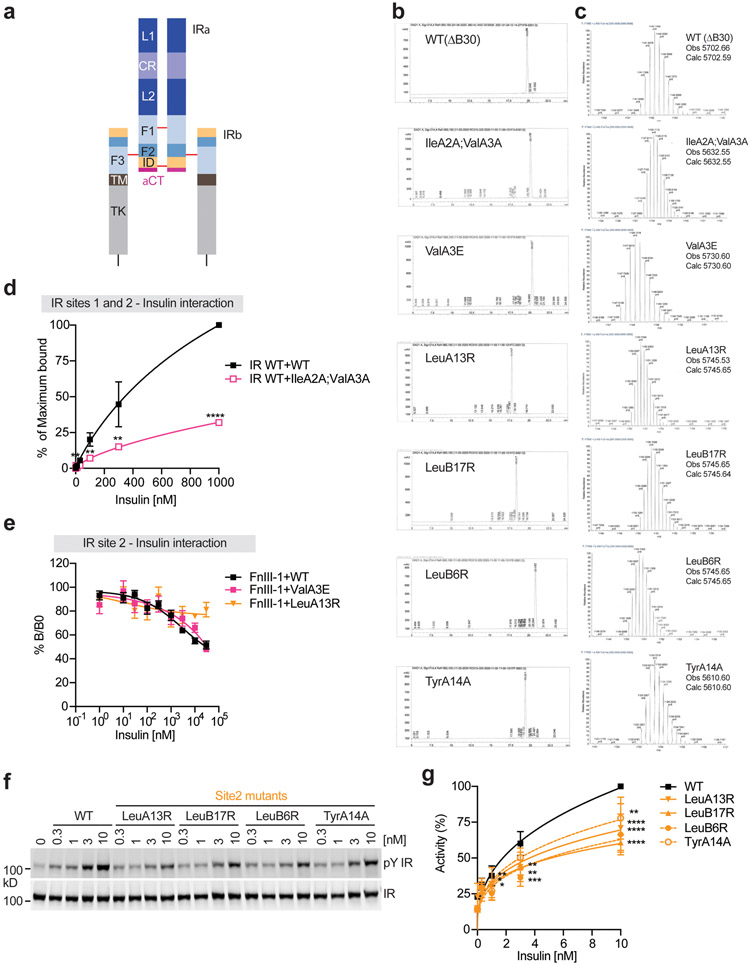
Extended Data Fig. 1. Domains of insulin receptor (IR) and activities of insulin analogs in primary mouse hepatocytes.
a. Domains and disulfide connectivity of IR. L1 and L2, leucine rich domains 1 and 2; CR, cysteine rich domain; F1, F2 and F3, fibronectin III (FnIII) domains; ID, insert in FnIII-2 domain; TM, transmembrane domain; TK, tyrosine kinase domain.
b. HPLC traces for each of the insulins synthesized and utilized for both functional and structural studies.
c. MS1 spectra of the purified insulins in B analyzed in the Orbitrap mass analyzer.
d. Binding of insulin WT and site-1 mutant (IleA2A;ValA3A) labeled with Alexa Fluor 488 to purified IR WT in the indicated conditions (Mean ± SD, WT, n=9 independent experiments; IleA2A;ValA3A, n=3). Significance calculated using two-tailed student t-test; **p<0.01 and ***p<0.001 (The exact p values are provided in the source data).
e. Insulin competition-binding assay for isolated FnIII-1 domain and insulin WT and mutants (ValA3E and LeuB17R) (Mean ± SD, n=3).
f. Insulin-induced IR autophosphorylation in 293FT cells expressing IR wild-type (WT). Cells were treated with the indicated insulin WT or site-2 mutants for 10 min. The IR autophosphorylation levels were assessed by quantitative western blotting with a phospho-tyrosine (pY) IRβ antibody. Expression levels of IRβ were monitored by anti-Myc blotting against the C-terminal Myc-tag.
g. Quantification of the western blot data shown in e (Mean ± SD). Each experiment was repeated four times. Significance calculated using two-tailed student t-test; *p<0.05; **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, and ****p<0.0001 (The exact p values are provided in the source data). Uncropped images for all blots and gels are available as source data.