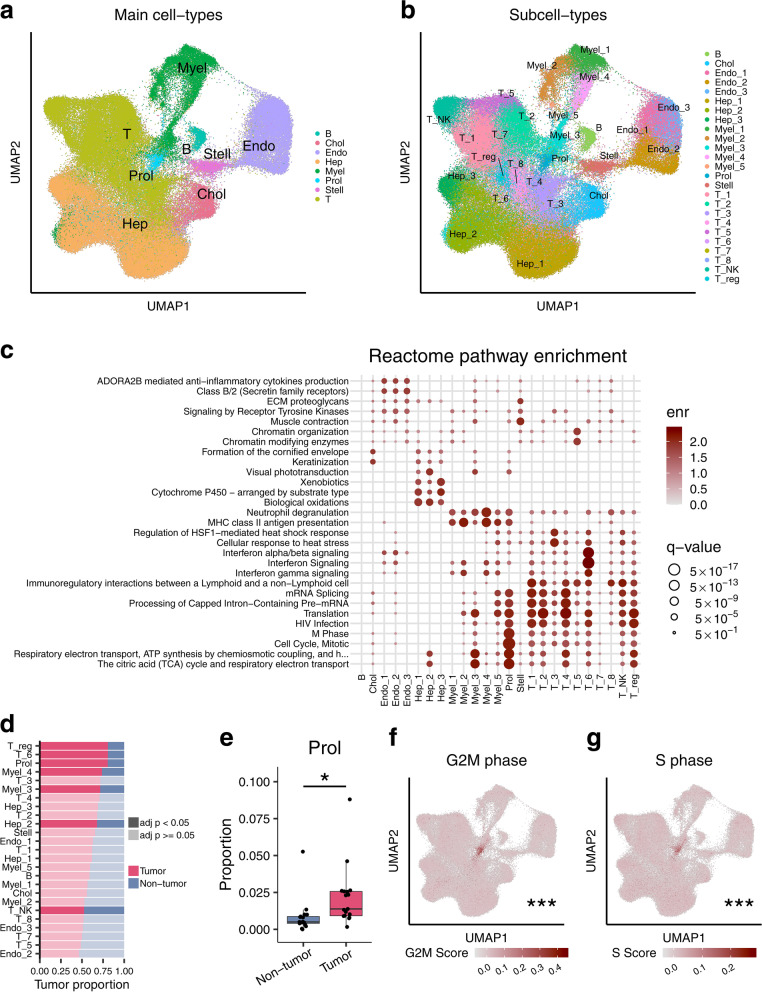
Fig. 1.
Multi-cohort integration of three liver HCC single cell level data sets identifies and characterizes an HCC-associated cell-type. We assessed liver cell-types and HCC-related cell-type changes by integrating Aizarani et al. [7] scRNA-seq data (n = 9 non-HCC samples), Sharma et al. [8] scRNA-seq data (n = 1 non-HCC, n = 14 HCC-tumor, and n = 14 adjacent non-tumor samples), and Rao et al. [25] snRNA-seq data (n = 3 HCC-tumor and n = 3 non-tumor samples). a, b Uniform Manifold Approximation and Projection (UMAP) visualization of 123,956 cells and nuclei integrated to remove cohort-specific effects. Clusters were assigned to (a) 8 major cell-types and (b) 25 subcell-types. c Pathway gene set enrichment analysis of the expression profiles for each subcell-type using the Reactome pathway database. The enr values indicate normalized enrichment scores and q-values denote Benjamini-Hochberg-adjusted p-values. Full pathway names are shown in Additional file 3: Table S2. d The bar plot shows the proportion of cells/nuclei in the full set of 123,956 cells/nuclei originating from HCC tumor and non-tumor samples separated by subcell-type. Darker fills indicate an FDR-adjusted p-value < 0.05 from a paired Wilcoxon test between proportions of HCC tumor and non-tumor samples. e Proportions of the Proliferative (Prol) cell-type are significantly higher in the 17 HCC tumor samples than in their 17 adjacent paired non-tumor samples after correcting for multiple testing with FDR, as assessed by a paired Wilcoxon test. f, g UMAP plots with cells/nuclei colored by their cell cycle score in the full single-cell level RNA-seq data of 123,956 droplets show that the Prol cluster consists of droplets with higher expression of (f) G2M phase genes and (g) S phase genes. The asterisks denote the significance of a difference between G2M and S phase gene scores between Prol and non-Prol cells/nuclei. Significance levels for p-values in (e–g) *p < 0.05, **p < 0.005, ***p < 0.0005. B indicates B cells; Chol, cholangiocytes; Endo, endothelial cells; Hep, hepatocytes; Myel, myeloid cells; Stell, stellate cells; and T, T cells