Fig. 2.
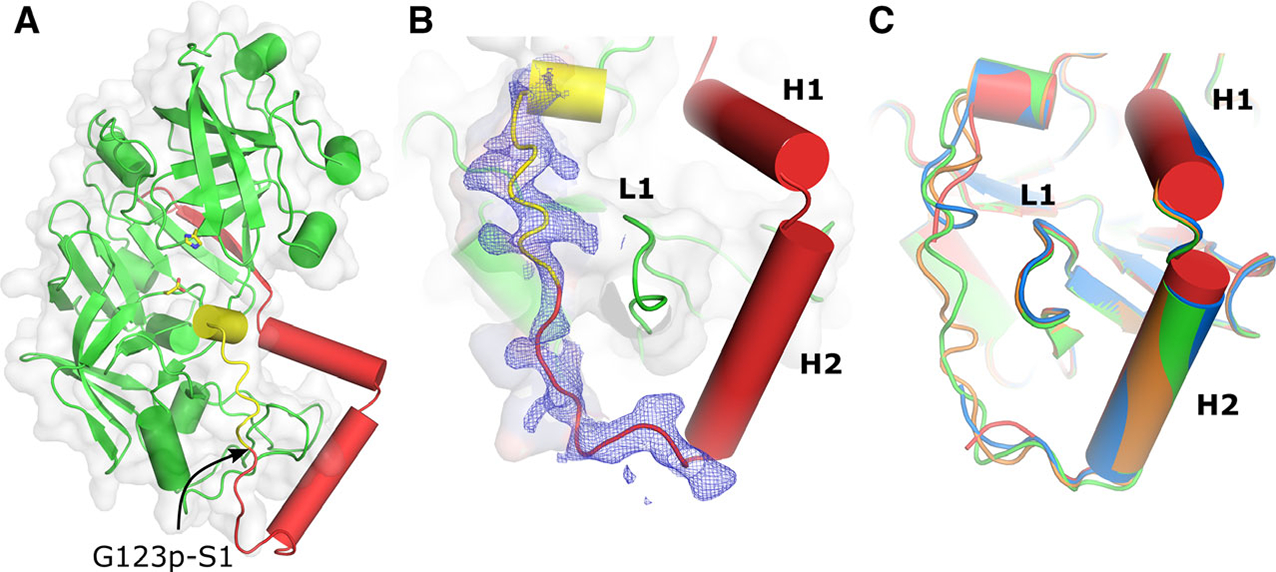
Structural fold and the secondary structure of the prosegment of pro-tPMs. (A) Overall structural fold of pro-tHAP. The prosegment is colored red and the polypeptide that would form the first β-strand of the mature enzyme is colored yellow. The active site residues are shown as sticks and an arrow indicates the native cleavage site. (B) 2Fo–Fc electron density (contoured at 0.8 σ) is shown around the promature region and the N terminus of the mature enzyme. The important secondary structure elements of the prosegment H1, H2, and L1 are also marked. (C) Conformational variabilities of the pro-mature regions of different pro-tHAP structures, HAP-zymo1 (green; 6KUB), HAP-zymo2 (orange; 6KUC), HAP-zymo3 (blue; 6KUD) from the current study and from the previously reported structure (red; 3QVC). The protein structural representations have been generated with the PyMOL molecular graphics system (Schrödinger LLC, New York, NY, USA; version 2.3.2).
