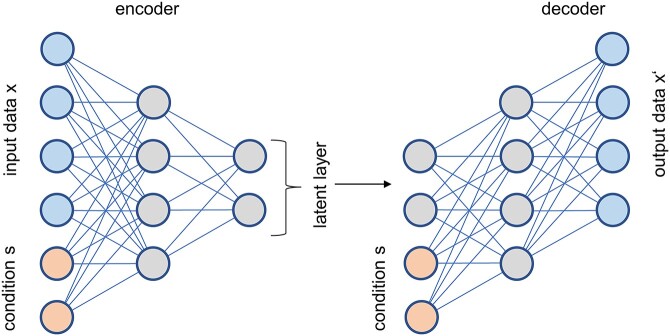
Figure 3.
Overview of the trVAE. The encoder part of the neural net processes input data plus information about the condition (smiling, cell type, etc.) and generates a compressed latent layer. The decoder uses this latent layer together with information about the condition to produce an output. During training, the condition fed to the encoder and the decoder are the same, while during prediction, the decoder receives the new condition for which an output should be generated. In contrast to a standard conditional VAE, an additional constraint is imposed on the first layer of the decoder for further regularization, the details of which we omitted here. While two input nodes are needed for the condition if an unary (‘one-hot’) encoding is used, the number of nodes in the other parts of the neural nets is far larger than shown here, for any realistic application. The diagram is redrawn from [30].