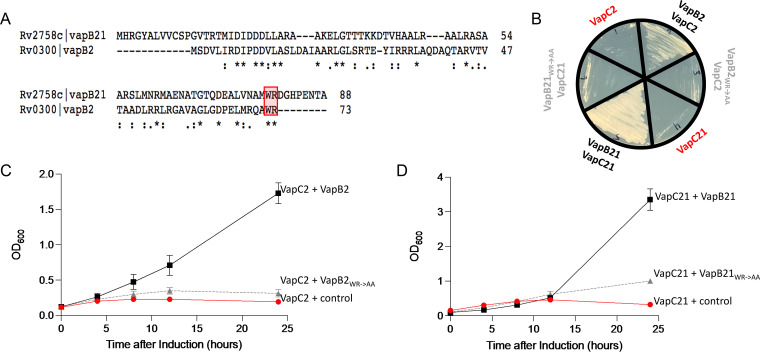
FIG 5.
The C-terminal WR residues of VapB2 and VapB20 antitoxins are necessary for inhibition of the cognate VapC toxin. (A) VapB2 and VapB21 sequence alignments highlighting the position of the WR residues generated using Clustal Omega v. 1.2.4 (45). (B) Growth phenotypes of a colony used to inoculate each of the represented growth profiles in panels C and D; color coding matches detailed descriptions in the growth profiles. (C) Growth profiles of M. smegmatis expressing VapC2 toxin from the ATC-inducible pMC1s plasmid plus either the empty isovaleronitrile (IVN)-inducible pNIT plasmid (control, red circle), wild-type VapB2 antitoxin in pNIT (black square), or VapB2 W72A/R739778A mutant antitoxin in pNIT (WR→AA, gray triangle). (D) Growth profiles of M. smegmatis expressing VapC21 from the ATC-inducible pMC1s plasmid plus either the empty IVN-inducible pNIT plasmid (control, red circle), wild-type VapB21 antitoxin in pNIT (black square), or VapB21 (W79A/R80A) mutant antitoxin in pNIT (WR→AA, gray triangle). Growth curves performed in triplicate; standard deviation indicated.