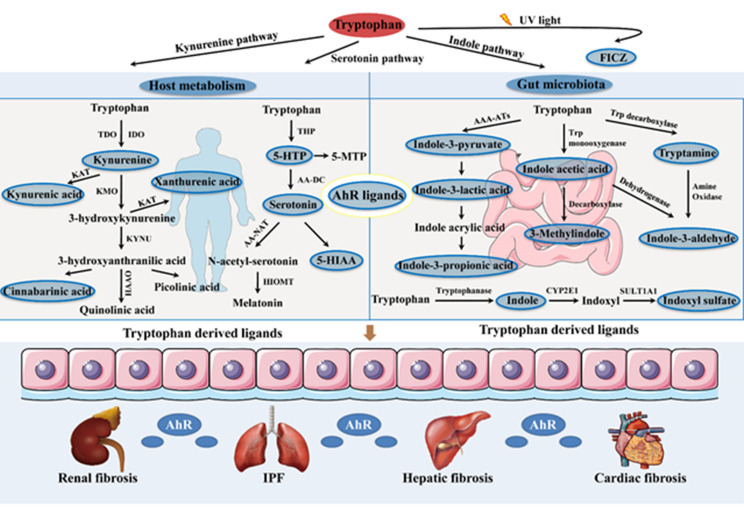
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of the effect of tryptophan metabolism in age-related tissue fibrosis through AhR. Tryptophan is mainly metabolized through three pathways in the host and gut microbiota: the kynurenine pathway, serotonin pathway and indole pathway. The endogenous ligands for AhR that are surrounded in blue, including FICZ, kynurenine, kynurenic acid, xanthurenic acid, cinnabarinic acid, 5-HTP, serotonin, 5-HIAA, indole-3-pyruvate, indole-3-lactic acid, indole-3-propionic acid, indole acetic acid, 3-methylindole, tryptamine, indole-3-aldehyde, indole and indoxyl sulfate, may modulate fibrosis progression after binding with AhR. AAA-ATs: aromatic amino acid aminotransferases; AA-DC: aromatic amino acid decarboxylase; AA-NAT: arylalkylamine N-acetyltransferase; CYP2E1: cytochrome P450 2E1; FICZ: 6-formylindolo[3,2-b]carbazole; HAAO: 3-hydroxyanthranilic acid oxygenase; 5-HIAA: 5-hydroxy- indole-3-acetic acid; HIOMT: hydroxyindole O-methyltransferase; 5-HTP: 5-hydroxy-tryptophan; 5-MTP: 5-methoxy-tryptophan; IDO: indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase; KAT: kynurenine aminotransferase; KMO: kynurenine 3-monooxygenase; KYNU: kynureninase; SULT1A1: sulfotransferase 1A1; TDO: tryptophan 2,3-dioxygenase; THP: tryptophan hydroxylase; Try: tryptophan.