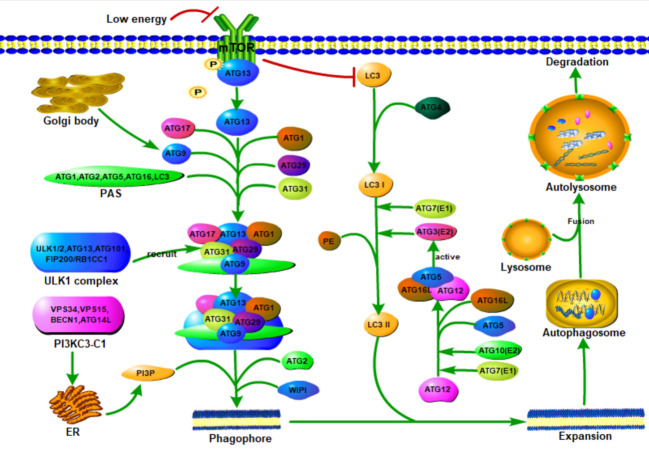
Figure 2.
The formation of autophagy. Autophagy is a multi-step process involving initiation, nucleation, expansion, fusion and degradation. When starvation or treatment with rapamycin, ATG13 dephosphorylates and binds to ATG17 in a mTOR protein-dependent manner and activates ATG1 to induce autophagy. Then ATG1 and ATG13 interact with ATG17, ATG29, and ATG31 complexes to form a PAS scaffold complex, which is a prerequisite step for the assembly of ATG protein downstream of PAS. The ULK/ATG1 complex is recruited into the membrane structure independently of PI3P and its downstream ATG protein, and then it is stabilized in the membrane structure by PI3P. ATG9 vesicles, deriving from the Golgi apparatus, can provide lipids required for downstream protein assembly of PAS, recruit ULK/ATG1 complexes, initiate autophagy and serve as a source of autophagosome membranes. Class III PI3K complex I (PI3KC3-C1) is necessary for the nucleation of autophagosomes and is composed of Vps34/VPS34, Vps15/p150, Vps30/BECN1 and Atg14/ATG14L. During autophagy induction, PI3KC3-C1, which produces PI3P on PAS, is recruited into PAS. PI3P transmits the received signal to the downstream ATG proteins through ATG18/WIPI protein. Two ubiquitin-like binding systems, the Atg8/LC3 system and the ATG12-ATG5-ATG16L system regulate the expansion and completion of autophagosomes. when starvation, mTOR protein is inactivated and starts LC3II transcription. LC3 is transformed into LC3I under the processing of ATG4, and then binds to PE under the catalysis of E1-like enzyme ATG7 and E2-like enzyme ATG3 (activated by ATG12-ATG5-ATG16L) and participates in the expansion and completion of autophagosome. After the phagocytic vesicles are expanded and expanded to form autophagosomes, only after the outer membrane of the autophagosomes fuse with the lysosome and complete the degradation of the contents by lysosomal hydrolases. The degraded substrate is eventually released into the cytoplasm for reuse. E1, ubiquitin-activating enzyme; E2, ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme; E3, ubiquitin ligase; ER, endoplasmic reticulum; PE, phosphatidylethanolamine.