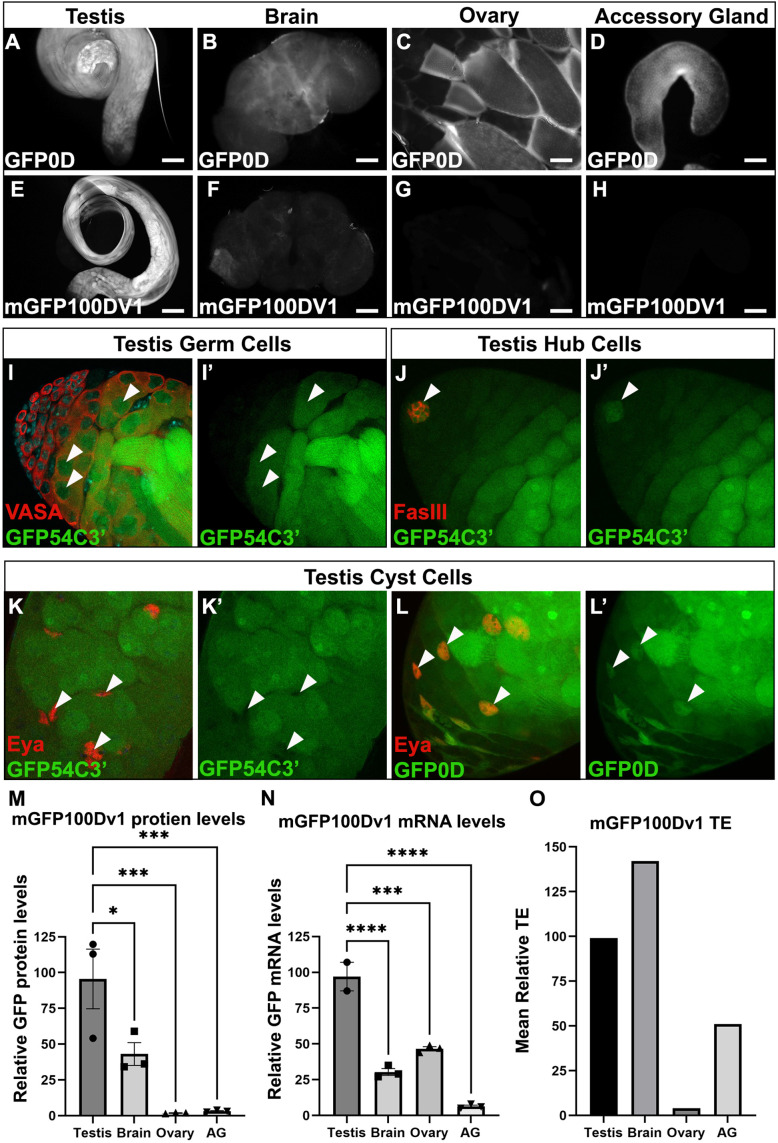
Figure 3. The adult testis and brain robustly express rare codon-enriched reporters.
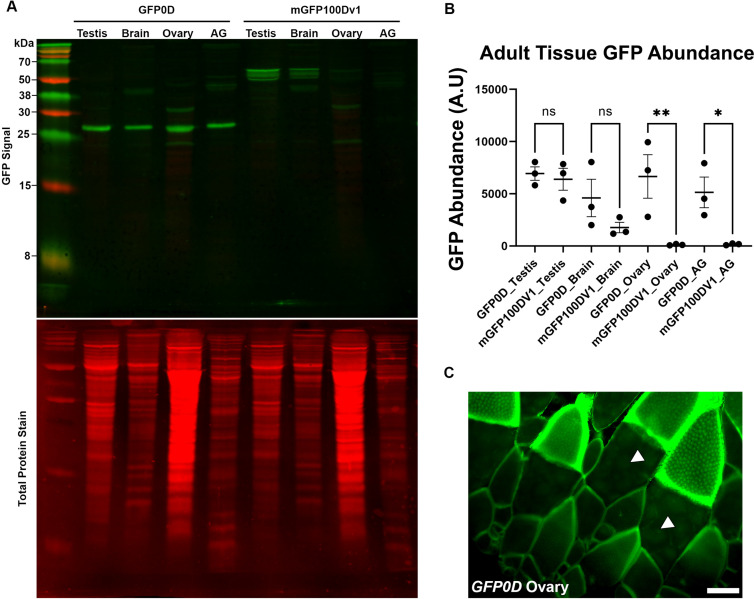
(A–D) Representative fluorescent images of dissected GFP0D adult tissues. Images are taken under identical conditions with fluorescence intensity normalized to testis. (E–H) Representative fluorescent images of dissected mGFP100Dv1 adult tissues. Images are taken under identical conditions with fluorescence intensity normalized to testis. (I–L’) Confocal images of adult GFP54C3’ testis immunostained with antibodies recognizing the indicated cell types. Arrowheads indicate cells of interest, I, I’ = germ cells, J, J’=hub, K, K’=somatic cyst cells. Right image in each pair shows the GFP only channel from the left image in the pair. (L’L’) Confocal image of adult GFP0D testis immunostained with Eya. Arrowheads = somatic cyst cells. (L’) GFP only channel of image in (L) (M) mGFP100Dv1 protein abundance in dissected adult tissues measured by western blot and plotted as a percentage relative to GFP0D (three replicates, N=10–12 animals each, plotting mean ± SEM, Dunnett’s multiple comparison to testis, *p<0.05, ***p≤0.001). See Figure 3—figure supplement 1 for representative blot image. (N) Steady state mRNA levels for heterozygous mGFP100Dv1/GFP0D expressing animals measured by Quantitative Real-Time PCR (qRT-PCR). mGFP100Dv1 mRNA levels are plotted as a percentage relative to GFP0D within each tissue. (2–3 replicates, N=10 animals each, plotting mean ± SEM, Dunnett’s multiple comparison to testis, ***p=0.0001,****p<0.0001). (O) Translation efficiency of mGFP100Dv1 in each tissue plotted as a percentage relative to GFP0D, plotting mean value. See Methods for details. Scalebars are 100 µm. AG = accessory gland.