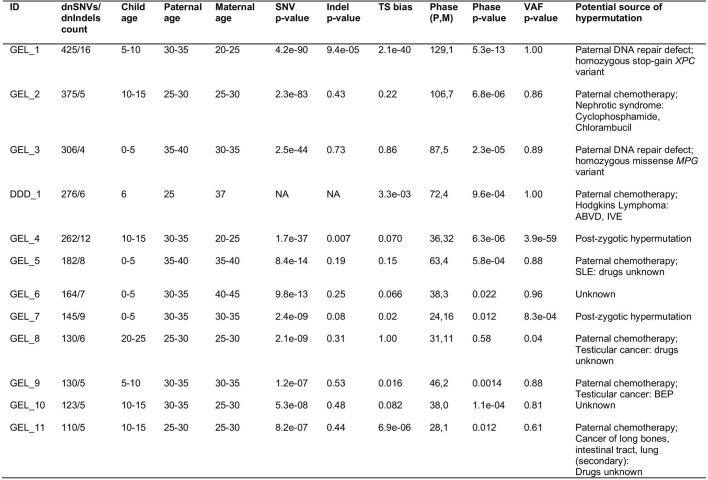
Extended Data Table 1.
Properties and possible hypermutation sources for germline hypermutated individuals
Eleven of these individuals were identified in 100kGP as having a significantly large number of dnSNVs (GEL_1-GEL_11) and one hypermutated individual identified in the DDD study (DDD_1). The DNM counts are for autosomal DNMs only. Child age refers to age when sample was taken. Paternal and maternal age refer to age at child’s birth. All ages are given as 5 year ranges for 100kGP individuals and the exact age for the DDD individuals. SNV and indel p-value is from testing the number of dnSNVs and dnIndels compared to what we would expect after accounting for parental age. TS bias: transcriptional strand bias poisson two sided p-value for dnSNVS. Phase (P,M): the number of dnSNVs that phase paternally (P) and maternally (M). Phase p-value: from two sided Binomial test for how different this ratio is compared to the observed proportion across all DNMs that phase paternally in 100kGP (~0.78). VAF p-value: one-sided Binomial p-value for testing if number of DNMs with VAF < 0.4 is greater than for all DNMs across 100kGP (~0.21). For potential sources of hypermutation when we suspect parental chemotherapy we have detailed the parental cancer and chemotherapy drugs received when relevant. The treatments are abbreviated as follows: BEP (Bleomycin, etoposide and platinum), ABVD (Bleomycin-Dacarbazine-Doxorubicin-Vinblastine) and IVE (Iphosphamide, epirubicin and etoposide).