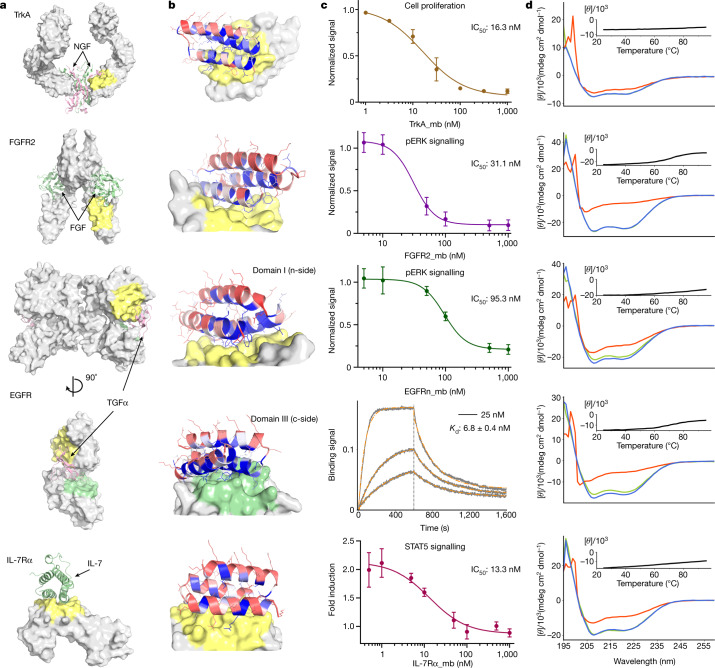
Fig. 3. De novo design and inhibition of native signalling pathways by designed miniproteins.
See the panel descriptions in Fig. 2 legend for a, b, d. The PDB identifiers are 2IFG (TrkA), 1DJS (FGFR2), 1MOX (EGFR) and 3DI3 (IL-7Rα) for a. c, For TrkA, the dose-dependent reduction in cell proliferation after 48 h of TF-1 cells with increasing TrkA minibinder (TrkA_mb) concentration is shown. (8.0 ng ml–1 human β-NGF was used for competition). Titration curves at different concentrations of NGF and the effects of the miniprotein binders on cell viability are presented in Extended Data Fig. 8. For FGFR2, the dose-dependent reduction pERK signalling elicited by 0.75 nM β-FGF in human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) with increasing FGFR2 minibinder (FGFR2_mb) concentration is shown. For the EGFRn-side binder, the dose-dependent reduction in pERK signalling elicited by 1 nM EGF in HUVECs with increasing EGFRn-side minibinder (EGFRn_mb) concentration is shown. See Extended Data Fig. 9 and Methods for experimental details. For the EGFRc-side binder, biolayer interferometry results are shown. See Extended Data Fig. 4 for the biolayer interferometry characterization results of the other optimized designs. For IL-7R, the reduction in STAT5 activity induced by 50 pM of IL-7 in HEK293T cells in the presence of increasing IL-7Rα minibinder (IL-7Rα_mb) concentrations is shown. The mean values were calculated from triplicates for the cell signalling inhibition assays measured in parallel, and error bars represent standard deviations. IC50 was calculated using a four-parameter-logistic equation in GraphPad Prism 9 software.