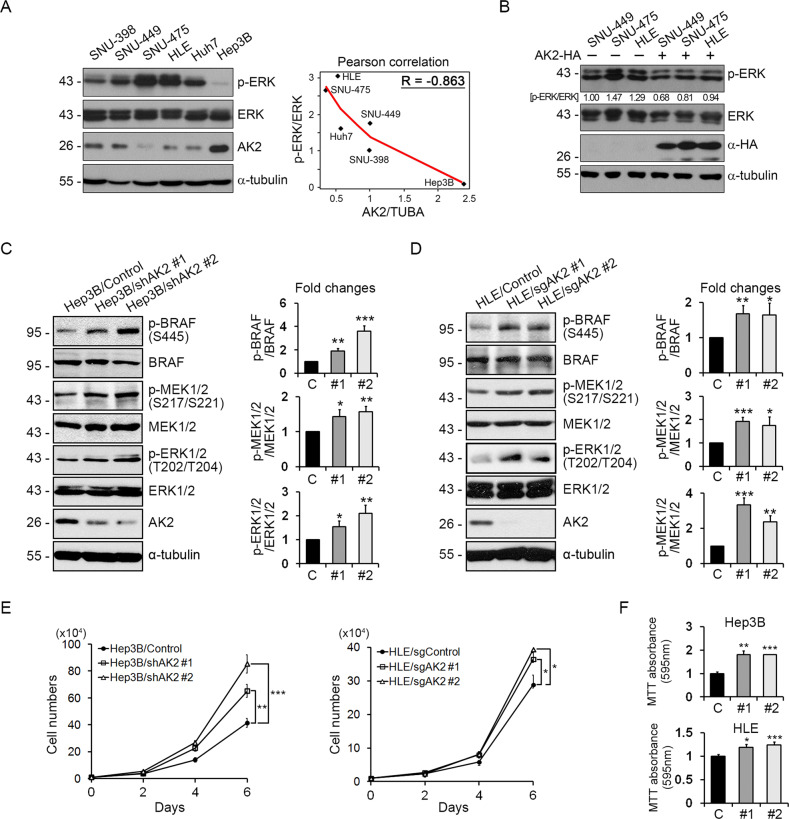
Fig. 3. AK2 loss enhances BRAF signaling to increase cell-proliferation and -migration in liver cancer cell lines.
A AK2 expression is down-regulated in liver tumor cell lines showing high p-ERK level. A panel of liver tumor cell lines (BRAF WT) was analyzed with western blotting (left). Total ɑ-tubulin was used as a loading control. The graph shows Pearson correlation between AK2/TUBA and p-ERK/ERK ratios. B Reconstitution with AK2 decreases p-ERK level. SNU-449, SNU-475, and HLE tumor cell lines were transfected with AK2-HA and assessed with western blotting. Total ɑ-tubulin was used as a loading control. The p-ERK/ERK ratios are denoted on the blots. C, D AK2 depletion enhances BRAF signaling in HCC cells. Hep3B/Control, Hep3B/shAK2, HLE/Control, and HLE/sgAK2 cells were analyzed with western blotting (left). Total ɑ-tubulin was used as a loading control. The signals on the blots were quantified and bars represent mean ± SD (n = 3) (right). E Hep3B and HLE cells and AK2 knockdown cells were monitored for cell proliferation for 6 days (104 cells at day 0). Values represent mean ± SD (n = 3). F Proliferations of Hep3B and HLE cells and AK2 knockdown cells were analyzed with MTT assay. Values obtained by 595 nm absorbance were relatively compared to control. Bars represent mean ± SD (n = 3).