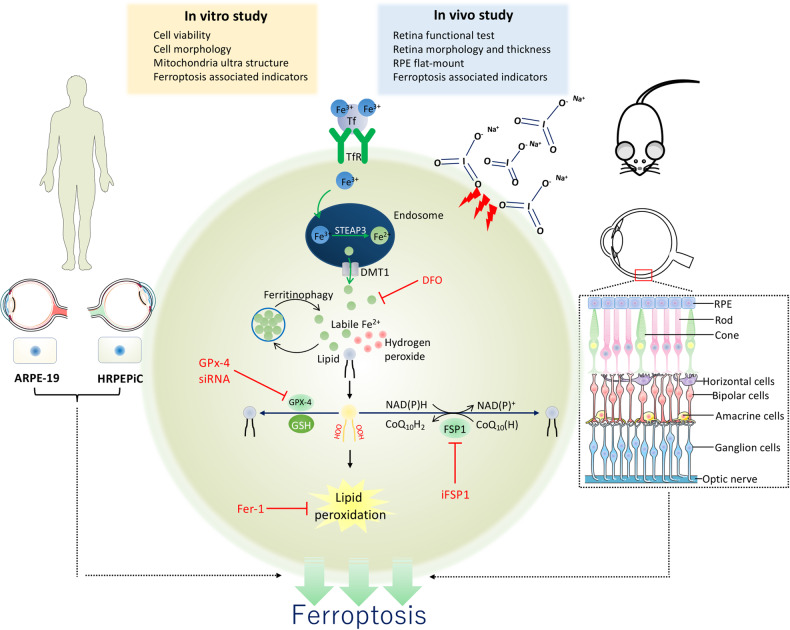
Fig. 8. A schematic diagram showing ferroptosis controls the fate of RPE cell death in SIO-induced RPE degeneration in vitro and in vivo.
Tf Transferrin, TfR Transferrin receptor, Fe3+ Ferric iron, Fe2+ Ferrous, STEAP3 Six-Transmembrane Epithelial Antigen Of Prostate 3, DMT1 Lipid, ROS Lipid reactive oxygen species, GPx-4 Glutathione peroxidase-4, GSH Glutathione, DFO Deferoxamine, Fer-1 Ferrostatin-1, OOH Hydroperoxides. The exposure of SIO increased labile iron, which interacts with lipid and hydrogen-peroxide thereby causing Fenton reaction and lipid peroxidation. GPx-4 relies on GSH to eliminate lipid ROS. DFO and Fer-1, two ferroptosis inhibitors, rescue RPE cell death induced by SIO. In contrast, GPx-4 siRNA aggravates SIO-induced RPE cell death. (Parts of the figure were drawn using pictures from Servier Medical Art (http://smart.servier.com/) (accessed on 28 June 2021), licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/) (accessed on 28 June 2021)).