Figure 2.
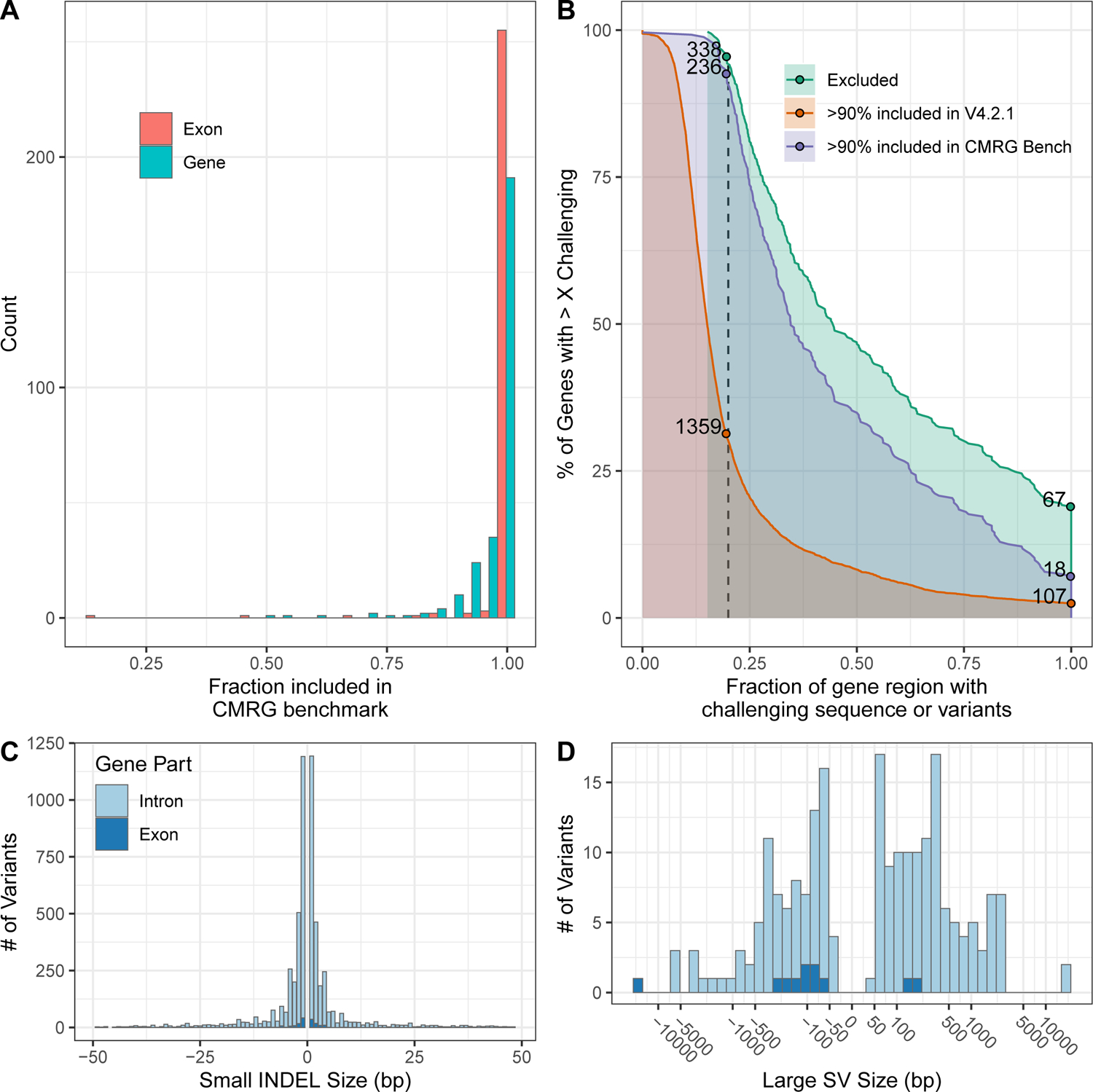
The new CMRG benchmark contains more challenging variants and regions than previous benchmarks. (A) Fraction of each gene region (blue) and exonic regions (red) included in the new CMRG small variant or SV benchmark regions. (B) Comparison of fraction of challenging sequences and variants for genes included in the new CMRG benchmark vs. the previous v4.2.1 HG002 benchmark vs. genes excluded from both benchmarks. 99% of CMRG benchmark genes have at least 15% of the gene region with challenging sequences or variants. The catalog of repetitive challenging sequences comes from GIAB and the Global Alliance for Genomics and Health (see text). Challenging variants for HG002 are defined as complex variants (i.e., more than one variant within 10 bp) as well as putative SVs and putative duplications excluded from the HG002 v4.2.1 benchmark regions. C) Size distribution of INDELs in the small variant benchmark, which includes some larger INDELs in introns (light blue) and exons (dark blue). D) Size distribution of large insertions and deletions in the SV benchmark in introns (light blue) and exons (dark blue).
