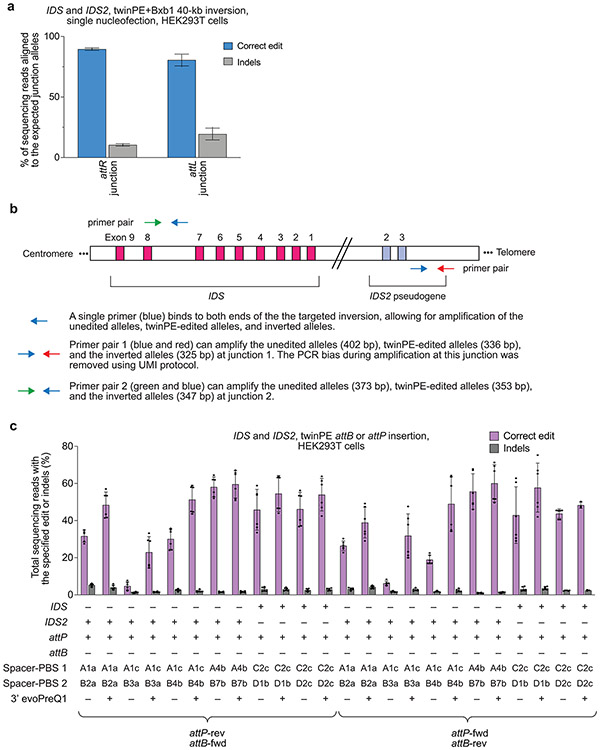
Extended Data Fig. 9. TwinPE and Bxb1 recombinase-mediated inversion between IDS and IDS2.
(a) Assessment of the inverted IDS junction purity by high-throughput sequencing in HEK293T cells. Frequency of expected junction sequences containing attR and attL recombination products after twinPE and BxB1-mediated single-step inversion. The product purities range from 81-89%. Values and error bars reflect the mean and s.d. of three independent biological replicates. (b) Schematic diagram of the designed PCR strategies for quantifying IDS inversion efficiency. Primer pair 1 (green forward and blue reverse primer) can amplify the unedited alleles (403 bp), twinPE-edited alleles (337 bp), and the inverted alleles (326 bp) at junction 1 in a single PCR reaction. Due to the size difference, a UMI protocol was applied to eliminate PCR bias during quantification of inversion efficiency. Similarly, using primer pair 2 (red forward and blue reverse primer), the unedited alleles (346 bp), twinPE-edited alleles (326 bp), and inverted alleles (320 bp) at junction 2 can be amplified in a single PCR reaction. Amplicons can then be sequenced by standard high-throughput sequencing protocols for amplicon sequencing. (c) Screening of pegRNA pairs for the insertion of Bxb1 attB and attP sequences at IDS and IDS2. TwinPE editing was tested with standard pegRNAs and epegRNAs containing a 3’ evoPreQ1 motif. Values and error bars reflect the mean and s.d. of three independent biological replicates.