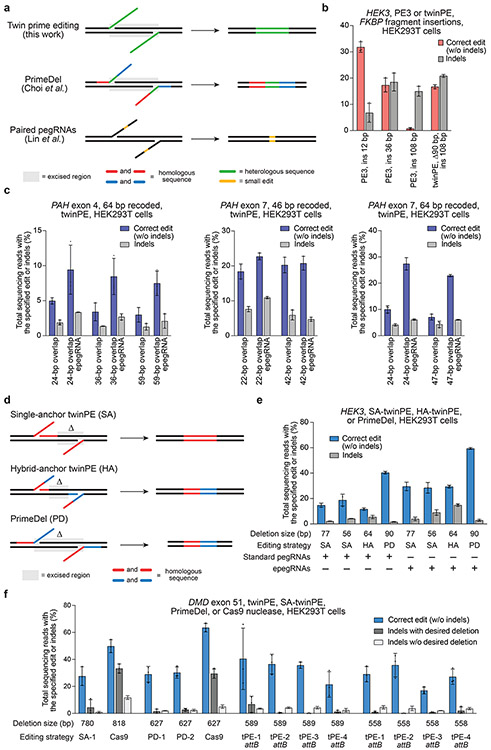
Figure 2 ∣. Targeted sequence insertion, deletion, and recoding with twinPE in human cells.
(a) Schematic diagram illustrating designs and edits generated for twinPE, PrimeDel36 and paired pegRNAs37. Shaded gray boxes indicate regions where DNA is excised, green lines indicate the incorporation of heterologous DNA sequence, red and blue lines indicate regions of sequence homology (red to red, blue to blue), and yellow lines indicate regions with small edits. PrimeDel can introduce but does not require introduction of heterologous sequence (green). (b) Insertion of FKBP coding sequence fragments with PE3 (12 bp, 36 bp, 108 bp) or twinPE (108 bp) at HEK3 in HEK293T cells. (c) Recoding of sequence within exons 4 and 7 in PAH in HEK293T cells using twinPE. A 64-bp target sequence in exon 4 was edited using 24, 36, or 59 bp of overlapping flaps, a 46-bp target sequence in exon 7 was edited using 22 or 42 bp of overlapping flaps, or a 64-bp sequence in exon 7 was edited using 24 or 47 bp of overlapping flaps. Editing activity was compared using standard pegRNAs or epegRNAs containing 3’ evoPreQ1 motifs. (d) Schematic diagram showing three distinct dual-flap deletion strategies that were investigated for carrying out targeted deletions. The “Single-anchor (SA)” twinPE strategy allows for flexible deletion starting at an arbitrary position 3’ of one nick site and ending at the other nick site. The “Hybrid-anchor (HA)” twinPE strategy allows for flexible deletion of sequence at arbitrarily chosen positions between the two nick sites. The “PrimeDel (PD)” strategy of Shendure and co-workers tested here allows for deletion of the sequence starting at one nick site and ending at another nick site. Shaded gray boxes indicate regions where DNA is excised, red and blue lines indicate regions of sequence homology (red to red, blue to blue). (e) Deletion of sequences at HEK3 in HEK293T cells using the SA-twinPE, HA-twinPE, or PD strategies targeting the same protospacer pair. Editing activity was compared using standard pegRNAs or epegRNAs containing 3’ evoPreQ1 motifs. (f) Deletion of exon 51 sequence at the DMD locus in HEK293T cells using SA-twinPE, PD, paired Cas9 nuclease, or twinPE-mediated attB sequence replacement. A unique molecular identifier (UMI) protocol was applied to remove PCR bias (see Supplementary Note 1). Values and error bars in (b-f) reflect the mean and s.d. of three independent biological replicates.