Fig. 2. HOXB13 interacts with HDAC3 protein through its MEIS domain.
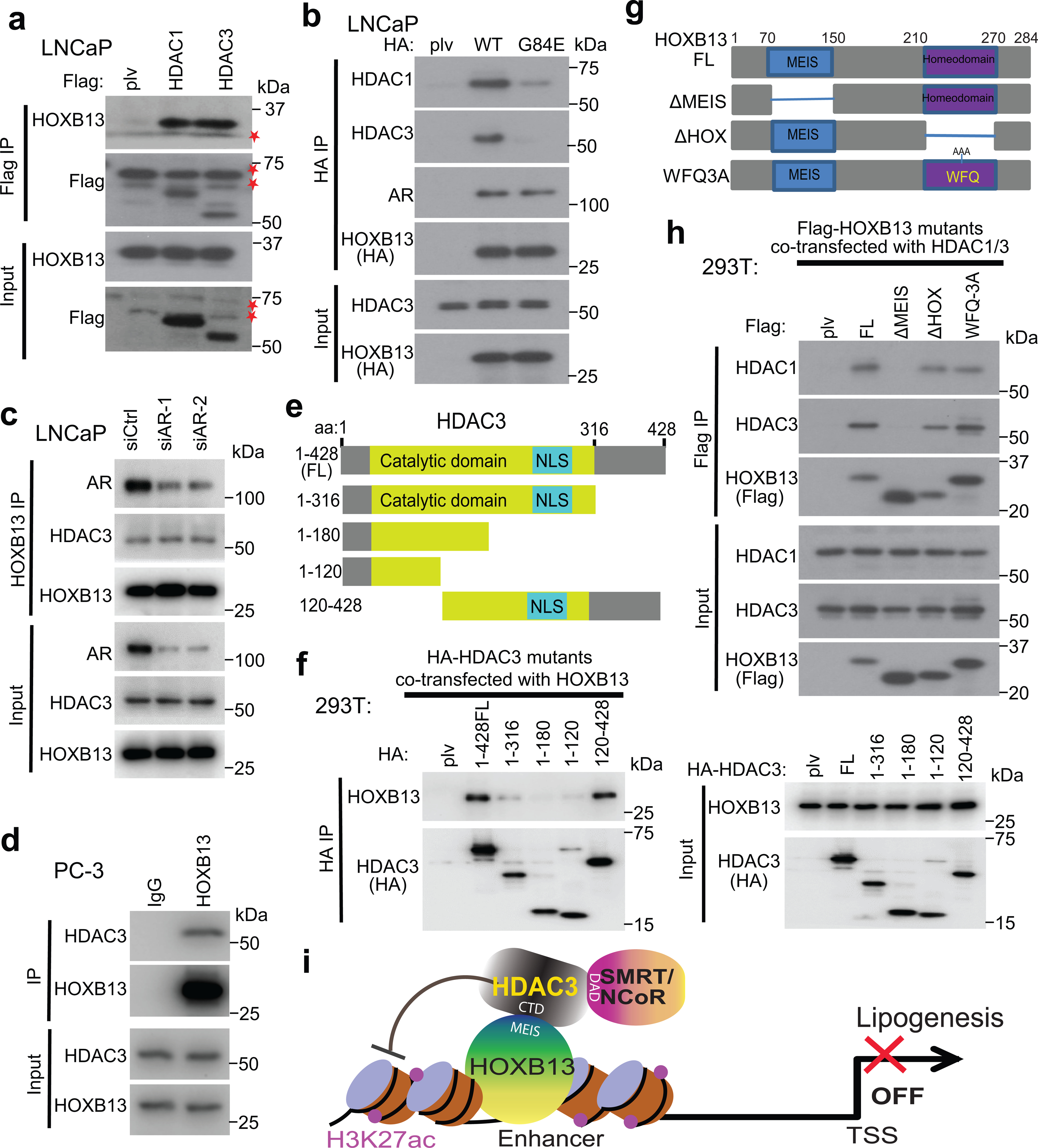
a. Co-IP of HDAC1 and HDAC3 shows interaction with HOXB13. Whole-cell lysates from LNCaP cells stably expressing Flag-tagged HDAC1 or HDAC3 were subjected to co-IP using anti-Flag antibody. The eluted co-IP complex was analyzed by WB, along with input controls. * indicates non-specific bands detected by anti-Flag antibody.
b. Cell lysates from LNCaP stably expressing HA-HOXB13 WT or G84E mutant were subjected to co-IP using an anti-HA antibody and then WB, along with input controls.
c. HOXB13 interaction with HDAC3 is not dependent on AR. Whole-cell lysates from LNCaP with control (siCtrl) or AR knockdown (siAR) were subjected to co-IP using an anti-HOXB13 antibody and then WB, along with input controls.
d. AR-negative PC-3 cells were subjected to co-IP using anti-HOXB13 or IgG control antibodies and then WB, along with input controls.
e-f. Co-IP of HA-HDAC3 FL or deletion constructs (e) transfected into 293T cells with coexpression of HOXB13 (f).
g-h. Co-IP of Flag-HOXB13 FL or deletion constructs (g) transfected into 293T cells with HDAC1 and HDAC3 co-expression (h).
i. A model depicting the interactions between HOXB13 and HDAC3/NCoR complex. CTD: C-terminal domain of HDAC3; MEIS: the MEIS domain of HOXB13; and DAD: the DAD domain of SMRT/NCoR.
