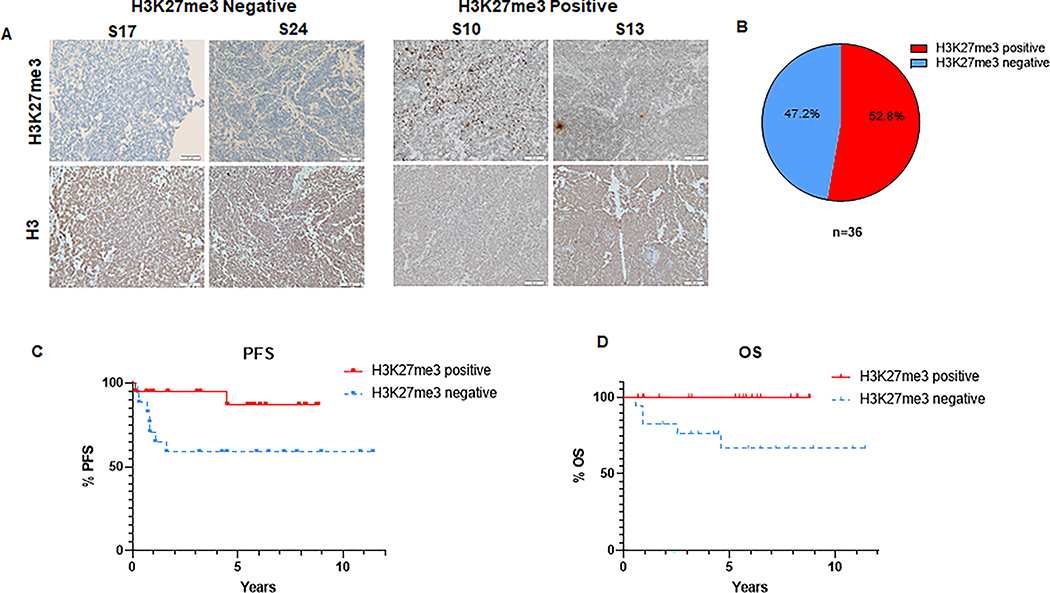
Figure 1: H3K27me3 status predicts clinical outcomes in group 3 and 4 medulloblastoma.
(A) Representative images of immunohistochemical (IHC) staining of H3K27me3 in tumor samples from non-WNT/SHH medulloblastoma patients (includes group 3 and 4 medulloblastoma). Representative images of H3K27me3-deficient tumors S17, S24 (left panel) and H3K27me3-proficient tumors S10, S13 (right panel) are shown. Lower panel shows the H3 staining of respective tumors (B) Pie chart demonstrating the proportion of H3K27me3-proficient versus H3K27me3-deficient tumors among the 36 analyzed samples from non-WNT/SHH medulloblastoma patients. (C) Kaplan-Meier graph showing the progression free survival (PFS) of non-WNT/SHH medulloblastoma patients following radiotherapy stratified by the H3K27me3 status (n=36), (p = 0.045). (D) Kaplan-Meier graph showing the overall survival (OS) of non-WNT/SHH medulloblastoma patients following radiotherapy stratified by the H3K27me3 status (n=36), (p = 0.014). (C-D) Median follow-up time was 5.8 and 6.8 years for H3K27me3-positive and H3K27me3-negative patients, respectively. Log-rank test was used for statistical analysis.