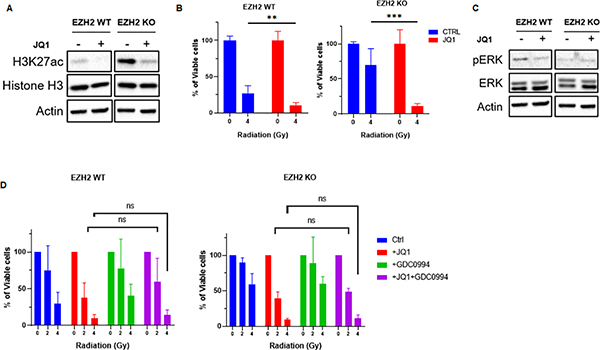
Figure 5. BET inhibition targets radiation resistance in H3K27me3-deficient medulloblastoma cells.
(A) WB analysis of indicated proteins in EZH2-WT and EZH2-KO #51 medulloblastoma cells that were mock-treated or treated with 0.1μM BET inhibitor JQ1 for 24h. (B) MTT assay showing percentage of viable cells l in EZH2-WT and EZH2-KO #51 medulloblastoma cells. Cells were mock-treated or pre-treated with 0.1μM BET inhibitor JQ1 for 24h and either mock-irradiated or exposed to indicated doses of IR. Percentage of viable cells l was determined 7d after IR. (C) WB analysis of indicated proteins in EZH2-WT and EZH2-KO #51 medulloblastoma cells that were mock-treated or pre-treated with 0.1μM BET inhibitor JQ1 for 24h and either mock-irradiated or exposed to 4Gy IR. Cells were harvested for WB analysis 24h following IR. Same cell lysates and, therefore same actin loading control was used as in Figure 5A. (D) MTT assay showing percentage of viable cells in EZH2-WT and EZH2-KO #51 medulloblastoma cells. Cells were mock-treated or pre-treated with 0.1μM BET inhibitor JQ1, 1μM ERK1 inhibitor GDC0994 or a combination of both for 24h and either mock-irradiated or exposed to indicated doses of IR. Percentage of viable cells was determined 7d after IR. (B, D) Data of three independent experiments are shown as mean +/− SD. Paired two-tailed T-test was used for statistical analysis (***p < 0.001; **p < 0.01; *p < 0.05).