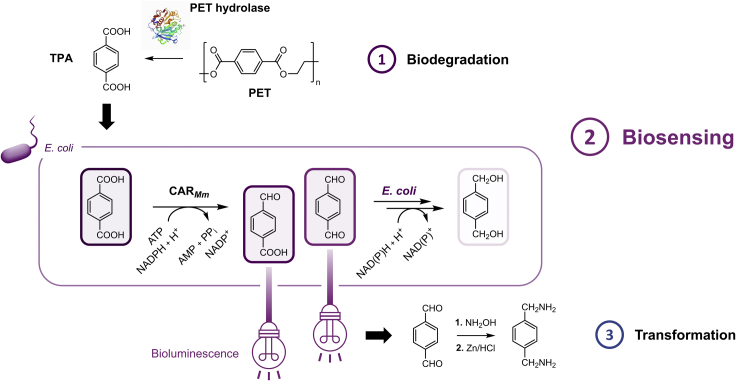
Figure 1.
Enzyme-coupled biosensor for the detection of TPA in E. coli
(1) The biocatalytic degradation of PET by hydrolases releases monomeric molecules including TPA and ethylene glycol (not shown). The PET hydrolase structure in the scheme was adapted from PDB: 6THT (Tournier et al., 2020). (2) TPA can be reduced to the corresponding dialdehydes and monoaldehydes by CARMm (accessory PPTNi not shown). These aldehydes are sensed by LuxAB, thereby emitting bioluminescence. Endogenous enzymes further reduce aldehydes to the corresponding primary alcohols. (3) The reactive TAL can be captured as aldoxime (not shown) and further converted to the diamine by reductive amination and basic work-up in a one-pot cascade, interconverting polymer precursors as future upcycling option after further optimization.