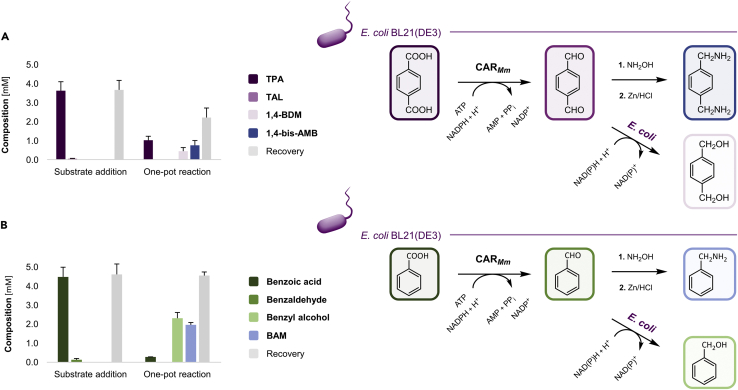
Figure 4.
Chemo-enzymatic one-pot cascades
Carboxylates are reduced by CARMm in RCs of E. coli BL21(DE3) to the corresponding aldehydes; PPTNi is omitted for clarity. In the presence of NH2OH · HCl, the oximes are formed (not shown), which are reduced to the primary amines (shades of blue) after the addition of Zn/HCl to the same reaction vessel.
(A) The TAL intermediate yields the desired 1,4-bis-AMB, besides 1,4-BDM as the major byproduct. Recoveries were reduced due to low solubility of TPA in RCM containing 5% (ν/ν) DMSO as organic co-solvent, the volatility of reaction compounds, and the formation of yet to be identified byproducts such as imines (Godoy-Alcántar et al., 2005; Simion et al., 2001).
(B) Benzoic acid in the presence of 5% (ν/ν) ethanol was reduced to benzaldehyde, yielding the desired BAM after reductive amination and benzyl alcohol as the sole byproduct. Experiments were performed in RCs (OD600 ≈ 10.0) co-expressing enzymes from pACYCDuet-1/carMm:pptNi (Bayer et al., 2021). Sampling: (1) after the addition of NH2OH · HCl (2.2 and 1.1 equiv for TPA and benzoic acid, respectively) and carboxylic acid and mixing; (2) after performing the reductive amination in one-pot. GC yields are presented as mean values + SD [mM] of biological replicates (n = 3). Performance was similar with RCs of E. coli RARE producing 27.2 ± 6.6% BAM and 13.1 ± 8.0% 1,4-bis-AMB (n = 2).