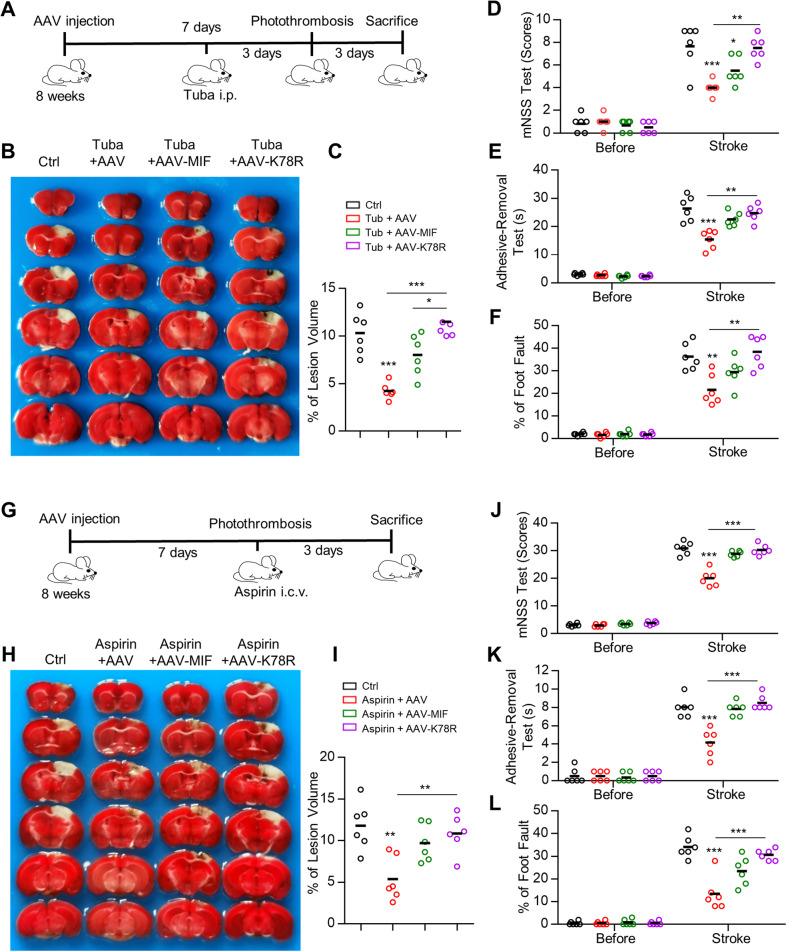
Fig. 5. HDAC6 inhibitor and aspirin protect neuronal death through increasing MIF acetylation after ischemia.
A Diagram of the experimental procedure. B HDAC6 inhibitor protects against ischemia-induced neuronal death through MIF acetylation. Mice were infected with either AAV-MIF-2A-mCherry or AAV-K78R-2A-mCherry and administered tubastatin A every day for 3 days. Ischemia was then induced and the infarct volume was analyzed by TTC staining in brain sections. C Quantification analysis of the lesion volume is shown in (B). Data shown were independent points and mean; one-way ANOVA, n = 6; *p < 0.05; ***p < 0.001. D–F Neurological deficits were evaluated by the mNSS test (D), adhesive-removal test (E), and foot fault assays (F). Data shown were independent points and mean; two-way ANOVA; n = 6; *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001. G Diagram of the experimental procedure. H Aspirin protects against ischemia-induced neuronal death through MIF acetylation. Mice were infected with AAVs and administered aspirin. Ischemia was induced and infarct volume was analyzed by TTC staining in brain sections. I Quantification analysis of the lesion volume is shown in (H). Data shown were independent points and mean; one-way ANOVA, n = 6; **p < 0.01. J–L Neurological deficits were evaluated by the mNSS test (J), adhesive-removal test (K), and foot fault assays (L). Data shown were independent points and mean; two-way ANOVA; n = 6; ***p < 0.001.