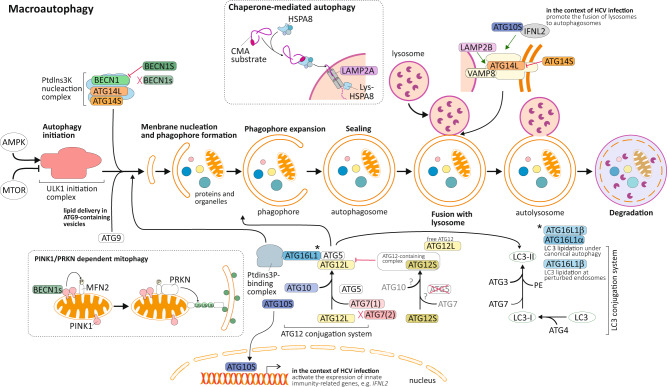
Fig. 3. Impact of alternatively spliced autophagy isoforms on autophagic process.
BECN1 as a subunit of the class III PtdIns3K nucleation complex contributes to autophagy initiation. A splice isoform, BECN1S, acts a negative regulator of autophagy induction. An additional splice variant, BECN1s, lacks function in the initiation of autophagy but supports PINK1- and PRKN/PARKIN-dependent mitophagy. A long and a short (lacking the homodimerization domain) splice isoform of ATG14 are reported. Whereas both isoforms can promote autophagy induction, they exert opposite effects on the regulation of autophagosome-lysosome fusion, with ATG14L endorsing but ATG14S restraining the formation of autolysosomes. Multiple components of the ATG12-conjugation system present splice isoforms. The presence of ATG12S, a short isoform of ATG12 which appears to be lacking the ability to form a covalent complex with ATG5, leads to the appearance of additional ATG12-containing complexes, beyond the ATG12–ATG5 complex, and the occurrence of free ATG12L, as well as reduced LC3 conjugation and autophagy flux. The ATG16L1 splice isoforms α and β, both allow the recruitment of the ATG12–ATG5 conjugate to the phagophore leading to the subsequent conjugation of LC3 proteins. The ATG16L1β isoform, with its unique lipid-binding region domain, also exerts an additional effect on LC3 lipidation at perturbed endosomes. In the context of hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection, a short ATG10 isoform, nuclear ATG10S, acting as a transcription factor, activates IFNL2/IL28A gene expression; IFNL2 protein in turn together with cytoplasmic ATG12S enhances autophagosome-lysosome fusion. ATG7(2), a short splice isoform of the canonical ATG7(1), lacks the ability to bind to LC3 and promote its lipidation. LAMP2 codes for splice variants that differ in their transmembrane and cytosolic regions within the C terminus region and exert distinct functions. Whereas LAMP2A controls the translocation of chaperone-mediated autophagy substrates across the lysosomal membrane, LAMP2B and LAMP2C promote the formation of autolysosomes or contribute to selective types of autophagy.