Fig. 4. A transmembrane and C-terminal domain interface regulates NKCC1 activity.
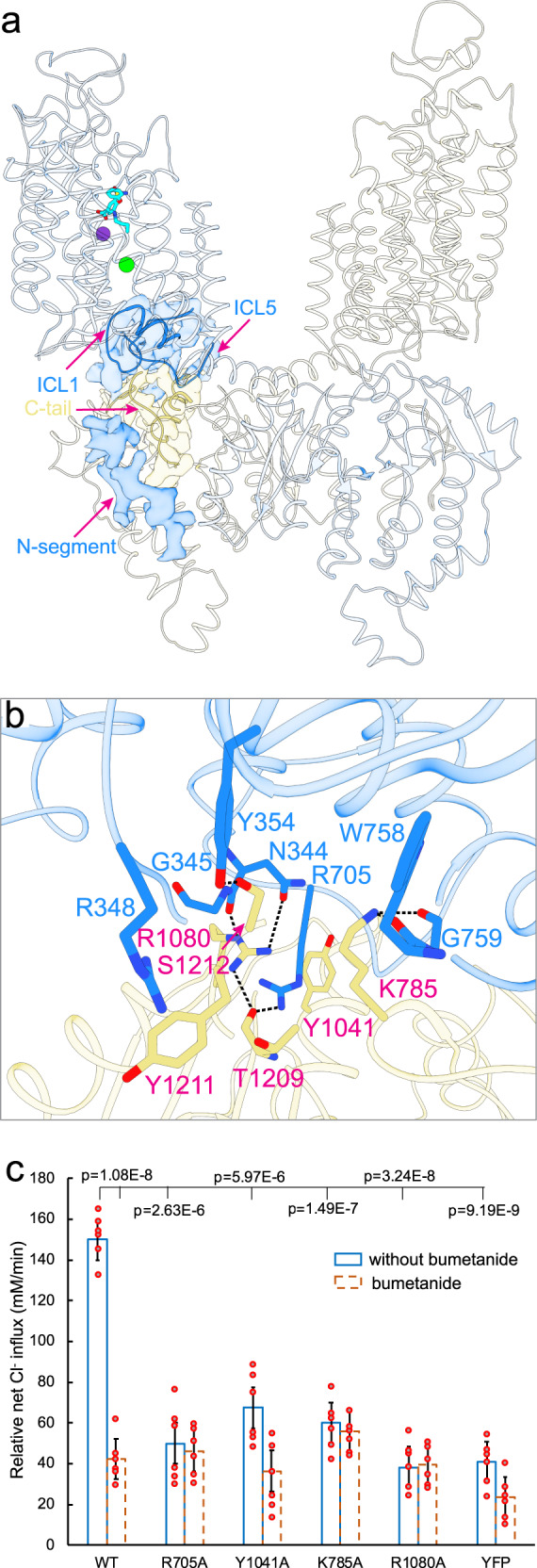
a A NKCC1 dimer structure highlights coupling among the N-terminal phosphoregulatory segment, extreme C-terminal tail, and ICL1. b The interface between the transmembrane (dodger blue) and a swapped C-terminal (khaki) domains is observed only in the herein described form of NKCC1iii/bumetanide dimer. Polar interactions are indicated as dashed lines. c Cl− transport rates in insect cells of wildtype human NKCC1 and mutants designed to disrupt the transmembrane and C-terminal domain interface. Each circle represents one kinetic measurement of a single sample in a 96 well plate. Unpaired one-tailed Student’s t tests are used for statistical analyses (n = 6; data are presented as mean values ± SD).
