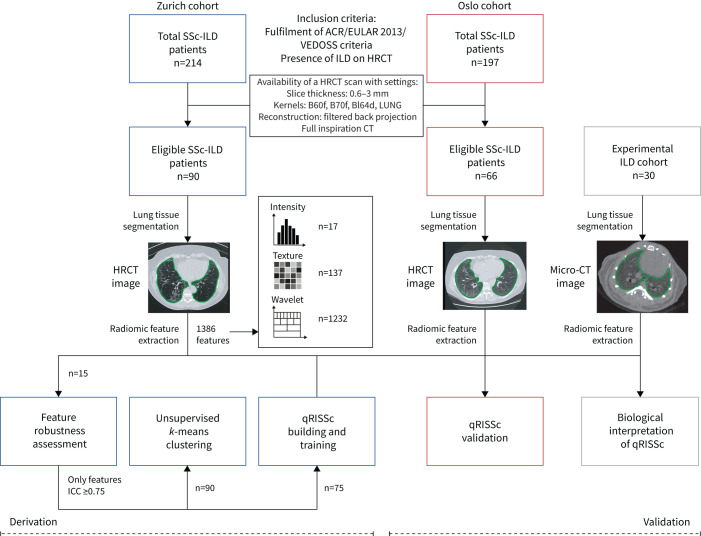
FIGURE 1.
Study workflow. We applied radiomics to three different datasets, including two independent cohorts of systemic sclerosis-associated interstitial lung disease (SSc-ILD) patients from University Hospital Zurich (derivation cohort) and Oslo University Hospital (validation cohort), and one experimental ILD cohort composed of 30 bleomycin-treated mice for association studies with biological features (i.e. proteomic, histological and gene expression data). Patients were retrospectively selected based on the fulfilment of early/mild SSc according to the Very Early Diagnosis of Systemic Sclerosis (VEDOSS) criteria [16] or established disease according to the 2013 American College of Rheumatology/European League against Rheumatism (ACR/EULAR) classification criteria [17], presence of ILD on high-resolution computed tomography (HRCT) as determined by a senior radiologist and predefined quality criteria for their HRCT images. For every subject, in total, 1386 radiomic features were extracted from semiautomated segmented CT images, including 17 intensity, 137 texture and 1232 wavelet features, using our in-house-developed software Z-Rad. Filtering of robust radiomic features (intraclass correlation (ICC) ≥0.75), unsupervised clustering and construction of the quantitative radiomic ILD risk score (qRISSc) for progression-free survival in SSc-ILD were performed in the Zurich cohort. Independent and external validation of the qRISSc was performed using the Oslo cohort.