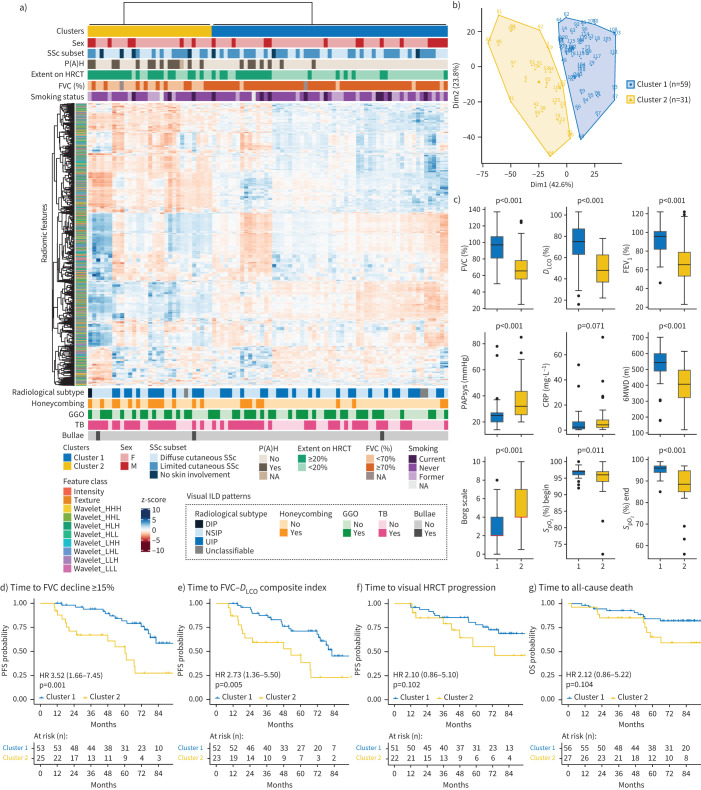
FIGURE 2.
Unsupervised k-means clustering of radiomic data from systemic sclerosis-associated interstitial lung disease (SSc-ILD) patients. a) Heatmap summarising the k-means clustering results (Zurich cohort, n=90). Before clustering, radiomic features were z-scored. Associations between the two identified radiomic patient clusters with categorical clinical parameters (top) and visual ILD patterns depicted on high-resolution computed tomography (HRCT) (bottom) are shown. b) k-means cluster plot indicating two stable clusters (Jaccard coefficient for cluster 1 (blue) 0.90 and for cluster 2 (yellow) 0.82, where 1 indicates perfect stability). c) Top row: box plots comparing lung function parameters between clusters 1 and 2 (forced vital capacity (FVC) % pred, diffusing capacity of the lung for oxygen (DLCO) % pred and forced expiratory volume in 1 s (FEV1) % pred); middle row: box plots showing systolic pulmonary arterial pressure (PAPsys), C-reactive protein (CRP) and 6-min walk distance (6MWD) for both clusters; bottom row: box plots indicating the Borg scale of perceived exertion (scale 0–10: 0=no exertion, 1=very weak, 2=weak, 3=moderate, 5=strong, 7=very strong, 10=extreme exertion) and peripheral oxygen saturation (SpO2) at the beginning and end of the test per patient cluster. d–f) Kaplan–Meier curves for progression-free survival (PFS) defined as either d) time to relative FVC decline ≥15%, e) time to FVC–DLCO composite index (relative decrease in FVC % pred of ≥15%, or a relative decline in FVC % pred of ≥10% combined with DLCO % pred of ≥15% according to [22]) or f) time to visual ILD progression on HRCT. g) Kaplan–Meier plot for overall survival (OS) defined as time to all-cause death. Hazard ratio (95% CI) and p-value of the univariate Cox regression are shown. P(A)H: pulmonary (arterial) hypertension; F: female; M: male; NA: not available; DIP: diffuse interstitial pneumonia; NSIP: nonspecific interstitial pneumonia; UIP: usual interstitial pneumonia; GGO: ground-glass opacification; TB: traction bronchiectasis.