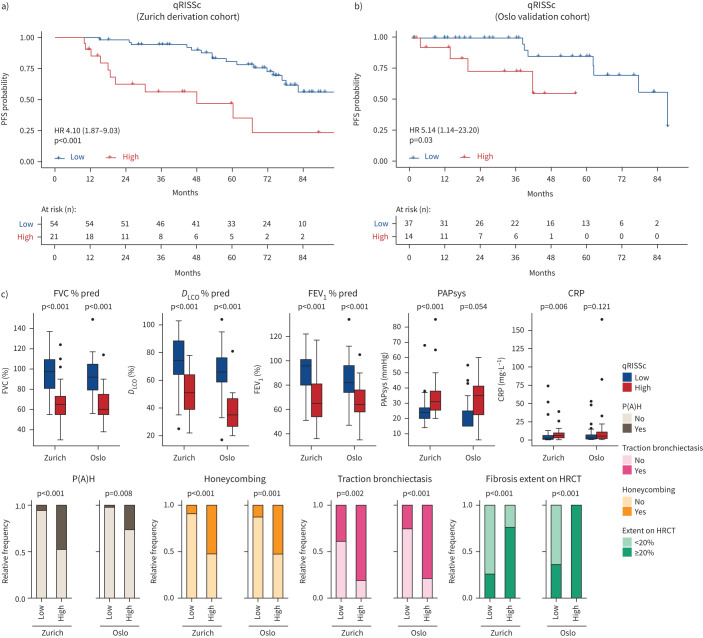
FIGURE 3.
Quantitative radiomic risk score (qRISSc)-based risk stratification for future lung function decline and associations of qRISSc with clinical parameters in the derivation and validation cohorts. a, b) Kaplan–Meier curves of the constructed quantitative radiomic interstitial lung disease risk score (qRISSc) for progression-free survival (PFS) defined as time to relative forced vital capacity (FVC) decline ≥15% in the a) derivation cohort from Zurich and b) external validation cohort from Oslo. Hazard ratio (95% CI) and p-value of the univariate Cox regression are shown. c) Significant associations of qRISSc with clinical parameters in both the derivation (Zurich) cohort and validation (Oslo) cohort. Fisher's exact test was used to compare categorical variables and the Mann–Whitney U-test was used to compare numerical variables. DLCO: diffusing capacity of the lung for carbon monoxide; FEV1: forced expiratory volume in 1 s; PAPsys: systolic pulmonary arterial pressure; CRP: C-reactive protein; P(A)H: pulmonary (arterial) hypertension; HRCT: high-resolution computed tomography.