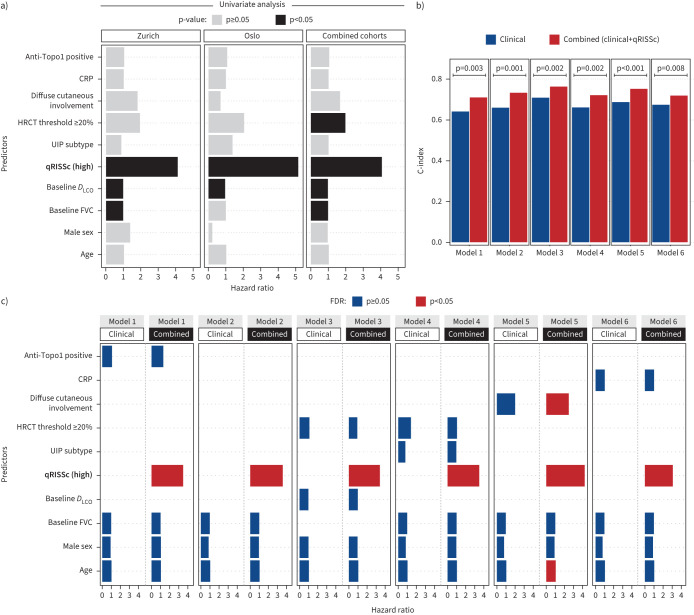
FIGURE 4.
Prognostic performance of the quantitative radiomic risk score (qRISSc) compared with other risk factors for systemic sclerosis-associated interstitial lung disease (SSc-ILD) progression. a) Bar plot indicating the results of the univariable Cox regression analysis of qRISSc compared with previously proposed clinical risk factors of SSc-ILD progression. b) Bar plot comparing the predictive power (C-index) of the multivariable models composed of the clinical risk factors of SSc-ILD progression alone (clinical models) versus models also incorporating qRISSc (combined models). Two-way ANOVA was used to compare model performances. Model 1: age+male sex+baseline forced vital capacity (FVC) (% pred)+anti-topoisomerase 1 (Topo1)±qRISSc; Model 2: age+male sex+baseline FVC (% pred)±qRISSc; Model 3: age+male sex+baseline diffusing capacity of the lung for oxygen (DLCO) (% pred)+high-resolution computed tomography (HRCT) threshold ≥20%±qRISSc; Model 4: age+male sex+ baseline FVC (% pred)+HRCT threshold ≥20%+usual interstitial pneumonia (UIP) subtype±qRISSc; Model 5: age+male sex+baseline FVC (% pred)+ diffuse cutaneous involvement±qRISSc; Model 6: age+male sex+baseline FVC (% pred)+C-reactive protein (CRP)±qRISSc. Models 1 and 4 (exclusively composed of clinical covariates) were overall not significant. c) Bar plot summarising the false discovery rate (FDR)-corrected results of the multivariable Cox regression analysis incorporating qRISSc (combined models) versus multivariable models composed of clinical risk factors alone (clinical models). Bars represent hazard radios for each predictor in each model, whereas colours indicate the p-value of the predictors corrected for multiple testing using the FDR. Covariates for univariable and multivariable Cox regression were selected based on literature evidence [2] and expert opinion.