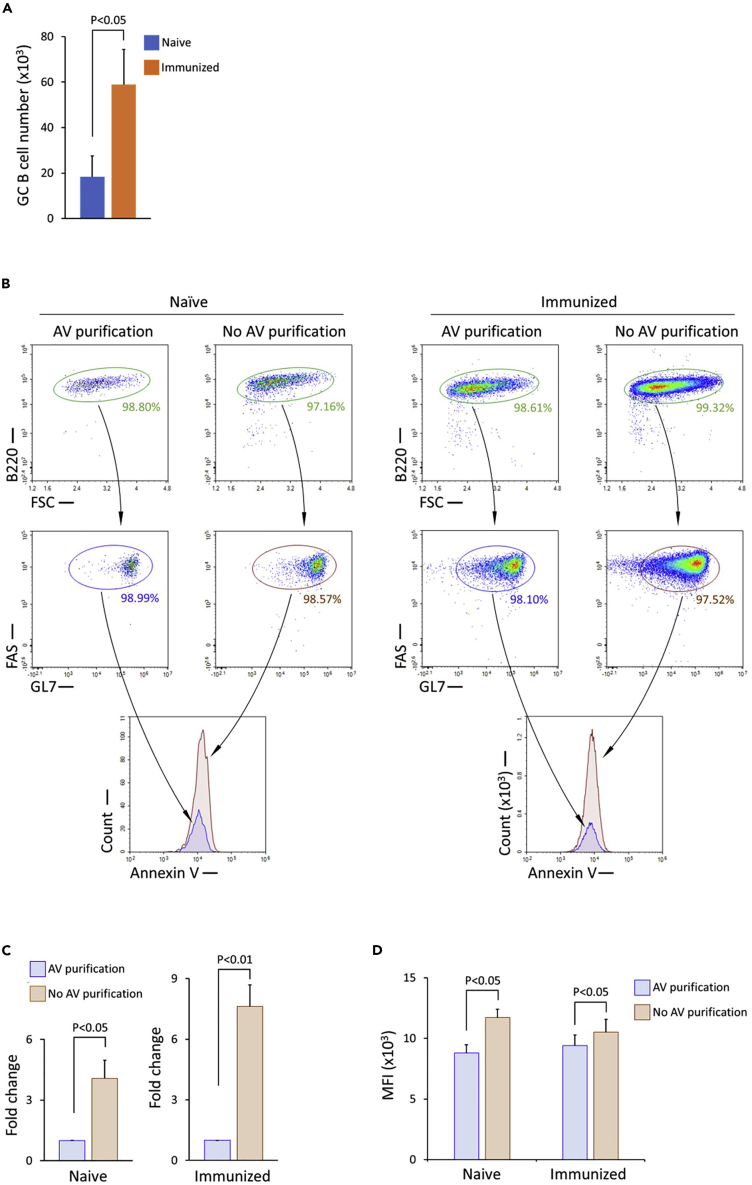
Figure 2.
Yield of GC B cells isolated from naive and immunized mice, and the effect of Annexin V-mediated negative selection on the yield
(A) Bar graph of normalized numbers of isolated GC B cells from one spleen of naive and immunized mice, depicting means with SEM error bars; 2-tailed T test; n= 8 biological replicates for immunized mice; n = 10 biological replicates for naive mice.
(B) Flow cytometry analysis of Annexin V staining intensity of purified GC B cells from naive mice (left) and immunized mice (right). The cells are separated into two halves for the treatment with and without Annexin V right before the step of Annexin V incubation to avoid the variances caused by the isolation steps prior to the Annexin V incubation. B cells are identified as B220+, and GC B cells are identified as B220+FAS+GL7+.
(C) Bar graph showing fold changes of isolated GC B cell numbers without Annexin V-mediated negative selection in naive and immunized mice, depicting means with SEM error bars; 2-tailed T test; n = 12 biological replicates for immunized mice; n = 4 biological replicates for naive mice.
(D) Bar graph of median fluorescence intensity (MFI) of Annexin V staining of GC B cells isolated from naive and immunized mice with and without Annexin V-mediated negative selection, depicting means with SEM error bars; 1-tailed T test; n = 10 biological replicates for immunized mice; n = 5 biological replicates for naive mice.