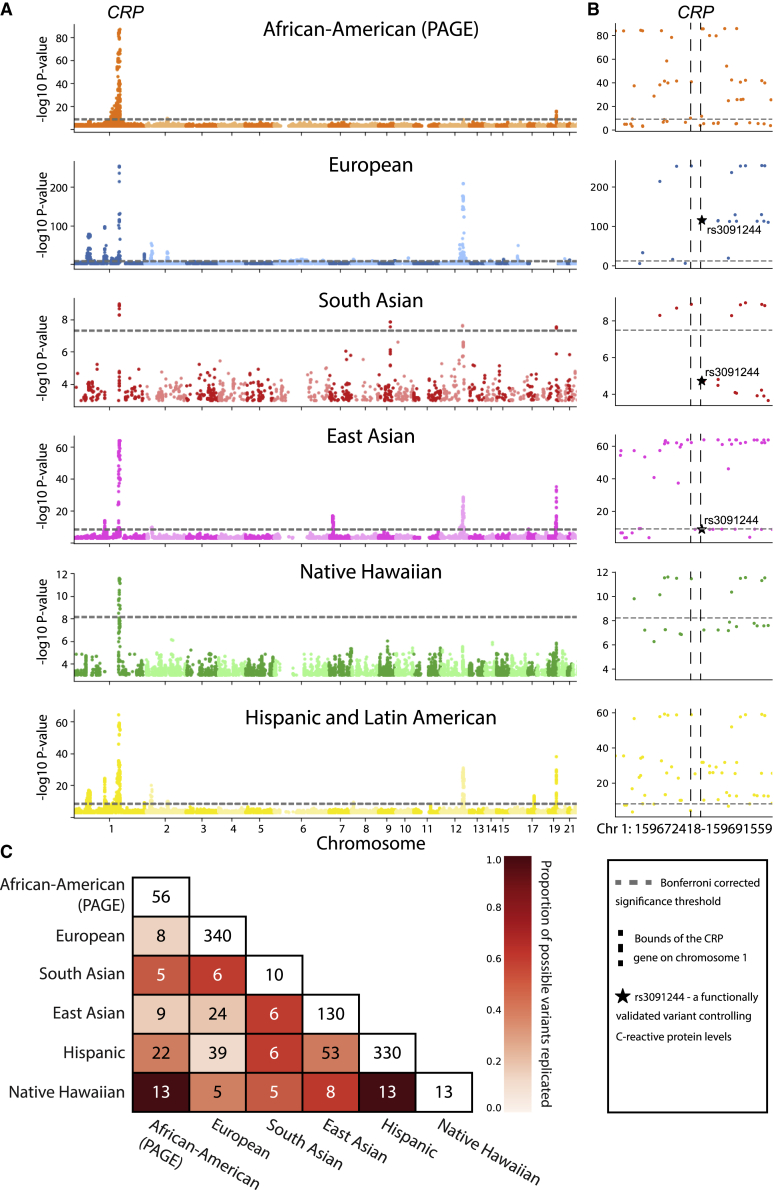
Figure 2.
C-reactive protein is an exceptional trait where standard GWA analyses may be sufficient to identify shared genetic architecture among ancestry cohorts
(A) Manhattan plot for SNP-level associations with C-reactive protein levels. Ancestry-specific Bonferroni-corrected significance thresholds are shown with dashed horizontal gray lines and listed in Table S11. Note that the scale of the − -transformed p values on the y axis is different for each ancestry for clarity.
(B) Manhattan plot of SNP-level associations around the CRP gene located on chromosome 1 for each ancestry (zoomed in from A). Boundaries of the CRP gene are shown with vertical dashed black lines. All six ancestries contain genome-wide significant SNPs in the region. Black stars in the European, South Asian, and East Asian plots represent rs3091244, a SNP that has been functionally validated as contributing to serum levels of C-reactive protein.55,56
(C) Heatmap of Bonferroni-corrected significant genotyped SNPs replicated between each pair of ancestries analyzed. Here, we focus on SNPs in the 1 MB region surrounding the CRP gene. Entries along the diagonal represent the total number of SNP-level associations in the 1 MB region surrounding the CRP gene for each ancestry. The color of each cell is proportional to the percentage of SNP-level associations replicated out of all possible replications in each ancestry pair (i.e., the minimum of the diagonal entries between the pairs being considered). For example, the maximum number of genome-wide significant SNPs that can possibly replicate between the Hispanic and East Asian is 25, and 20 replicate, resulting in the cell color denoting 80% replication. A similar matrix, computed including imputed SNPs, is shown in Figure S20.