Figure 3.
PRDM13 expression in neural progenitors in the developing cerebellum and brainstem
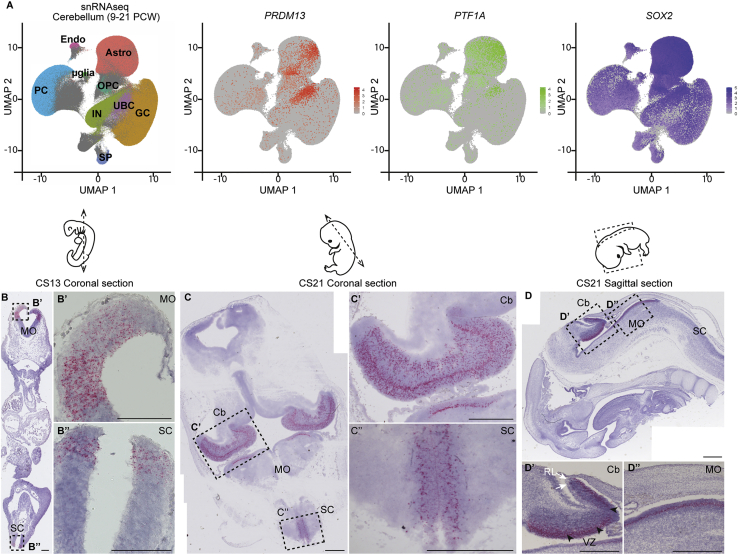
(A) Single-nucleus RNA-seq (snRNA-seq) data from human fetal cerebellum (9–21 PCW). snRNA-seq datasets were retrieved from the Human Gene Expression During Development Atlas25 (Descartes, https://descartes.brotmanbaty.org) and analyzed with the Seurat package. Cells are visualized on uniform manifold approximation and projection (UMAP) plots. In the first panel, cells are color-coded according to cell annotations from the Descartes Atlas (PCs, Purkinje cells; UBCs, unipolar brush cells; GCs, granule cells; INs, interneurons; Astros, Astrocytes; OPCs, oligodendrocytes precursors; μglia, microglia; SPs, SLC24A4_PEX5L_positive cells; Endos, vascular endothelial cells). In the three other panels, cells are colored in graded intensities, reflecting the expression levels of PRDM13, PTF1A, and SOX2.
(B–D) Detection of PRDM13 transcripts (red) by RNAscope in situ hybridization on coronal (B and C) or sagittal (D) sections through human embryos at Carnegie stage 13 (B) and 21 (C and D). (B′) and (B″), (C′) and (C″), (D′) and (D′) are higher magnifications of the regions outlined by dotted squares in (B), (C), and (D), respectively. At CS13, specific expression of PRDM13 is detected in the dorsal VZ of the caudal part of the hindbrain (Hb, B′) and in the dorsal VZ of the caudal neural tube (NT, B″). At CS21, PRDM13 starts to be expressed in the primordium of the cerebellum (Cb, C, C′) while being maintained in the medulla oblongata (MO, C, D, D″) and spinal cord (SC, C, C″). In the cerebellum (D′), PRDM13 is more specifically detected in the ventricular zone (VZ, black arrowheads), while it is absent from the rhombic lip (RL, white arrows). Scale bars: 100 μm (B) and 500 μm (C and D).