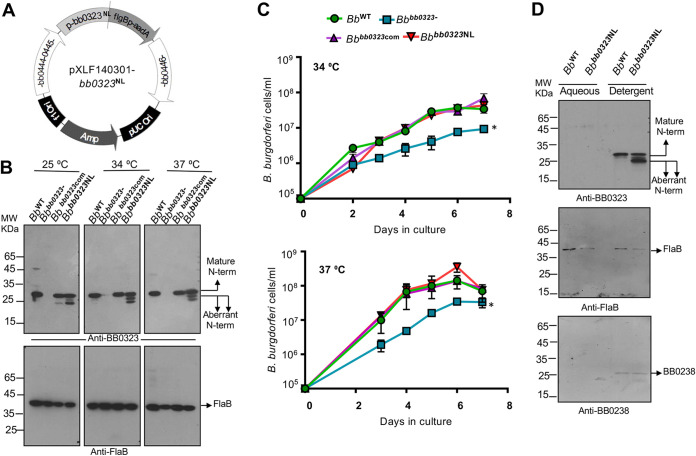
FIG 3.
Alteration of BbHtrA cleavage site in BB0323 impairs processing of N-terminal domains but does not affect spirochete growth and biology in vitro. (A) Diagram of the vector construct (pXLF14301-bb0323NL) for introducing mutants in B. burgdorferi. The construct was generated via the chromosomal insertion of bb0323N236AL237A into the bb0323 deletion mutant, in order to produce bb0323NL complemented B. burgdorferi isolates (designated Bbbb0323NL). (B) Production of mature N-terminal BB0323 domains in B. burgdorferi isolates. The wild type (WT), bb0323 mutant (bb0323-), bb0323 complement (bb0323com), and cleavage site mutant (Bbbb0323NL) were grown at different temperatures (25 to 37°C). The spirochetes were harvested and lysates were separated by SDS-PAGE, transferred onto a nitrocellulose membrane, and blotted with antiserum against BB0323-N (upper portion) and FlaB (lower portion). Mature N-terminal proteins with expected molecular weights of ∼27 kDa (larger arrows), as well as polypeptides of slightly lower molecular weights (small arrows), are indicated. (C) The Bbbb0323NL cleavage site mutants display normal growth in culture compared to wild-type cells. B. burgdorferi cells were diluted to a density of 105/mL and grown at 34°C and 37°C in BSK-H medium. Samples were counted under a dark-field microscope every 24 h using a Petroff-Hausser cell counter. The bb0323 deletion mutant (Bbbb0323-) display significant growth defects compared to other isolates (*, P < 0.05). (D) N-terminal BB0323 proteins are associated with spirochete membrane fractions. Spirochete lysates were subjected to Triton X-114 phase partitioning of aqueous and detergent phases and immunoblotted using antibodies against BB0323, FlaB, and BB0238.