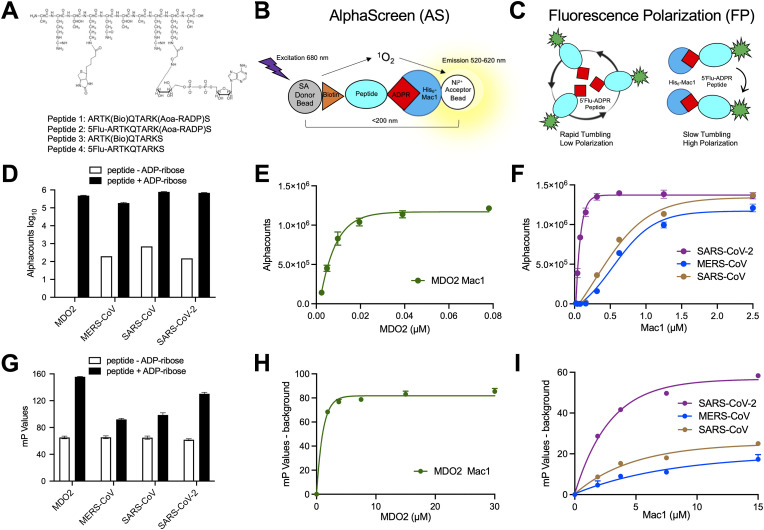
Fig. 1.
Coronavirus Mac1 binding to ADP-ribosylated peptides. (A) Illustration of the amino-oxyacetic acid modified lysine-conjugated ADP-ribosylated peptide with an additional biotin conjugated to a different lysine residue and included are the amino acid sequences and modification sites of peptides used in this study. (B–C) Cartoon diagrams depicting a bead-based AS (A) and FP (B) assays for measuring macrodomain interactions with an ADP-ribosylated peptide. (D) Macrodomain proteins were incubated with peptide #1 or peptide #3 for 1 h at RT and Alphacounts were determined as described in Methods. (E–F) Peptide #1 was incubated with indicated macrodomains at increasing concentrations and Alphacounts were measured as previously described. (G) Mac1 proteins were incubated at indicated concentrations with peptide #2 or peptide #4 and the plate was incubated at 25 °C for 1 h before polarization was determined. (H–I) Peptide #2 was incubated with indicated macrodomain proteins at increasing concentrations and polarization was determined as previously described. All data represent the means ± SD of 2 independent experiments for each protein.