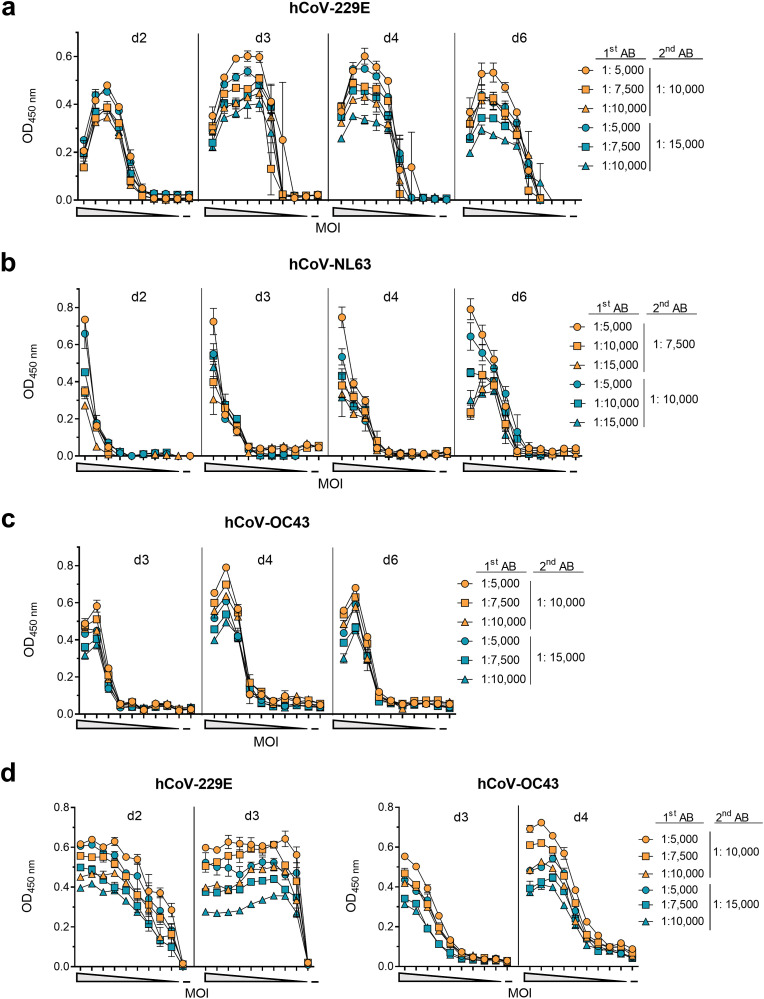
Fig. 3.
Detection of hCoV-229E, -NL63 and -OC43 infection by in-cell ELISA. For establishing optimal conditions for the in-cell ELISA, target cells were seeded and the following day inoculated with a 10-fold or 2-fold serial dilutions of the respective virus. a) hCoV-229E was inoculated onto Huh-7 cells at a maximum MOI of 0.44, b) -NL63 onto Caco-2 cells at a maximum MOI of 1.6, and c) -OC43 onto Huh-7 at a maximum MOI 0.35. d) hCoV-229E and -OC43 were titrated again 2-fold at maximum MOI of 0.004 or 0.006, respectively. At the indicated time points post infection, cells were fixed and permeabilized before cells were treated with different concentrations of anti-nucleocapsid primary antibody (1st AB) and subsequently with different concentrations of HRP-coupled secondary detection antibody (2nd AB). Optical density (OD) was measured at 450 nm and baseline corrected at 620 nm. Signals obtained 2 h post infection (input control) were subtracted from later time points. Data are shown as mean of duplicates ± range, performed once.