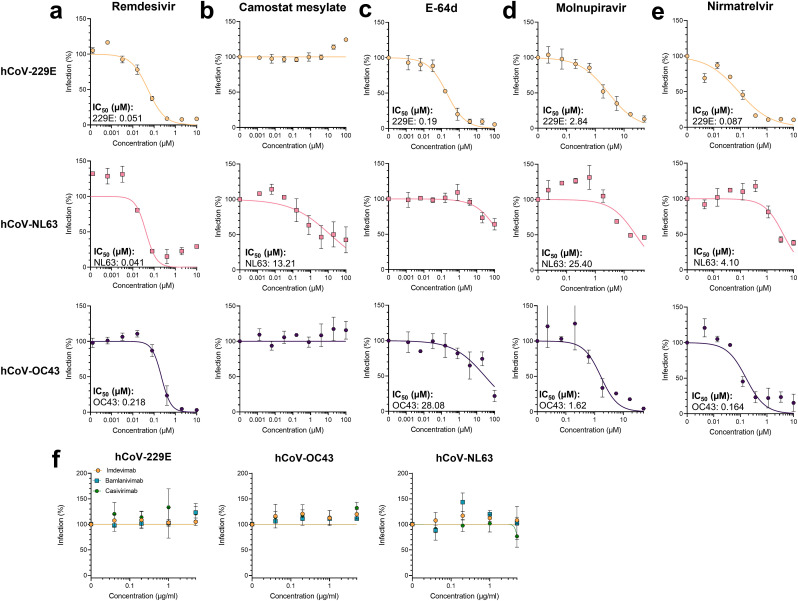
Fig. 5.
Application of in-cell ELISA to evaluate antivirals against hCoVs. To analyze compounds, target cells were treated with 5-fold serial diluted a) remdesivir, b) camostat mesylate, c) E-64d, d) molnupiravir or e) nirmatrelvir before inoculation with hCoVs. f) To analyze antibodies, virus was pre-incubated for 30 min with imdevimab, bamlanivimab, or casirivimab before inoculating target cells. hCoV-229E experiments were performed on Huh-7 cells at an MOI of 0.002 and infection determined by in-cell ELISA 2 days later. hCoV-NL63 experiments were performed on Caco-2 cells at an MOI of 0.01 and infection determined by in-cell ELISA 6 days later. hCoV-OC43 experiments were performed on Huh-7 cells at an MOI of 0.006 and infection determined by in-cell ELISA 3 days later. Data were normalized to untreated virus control (100%) and are presented as mean ± SEM of triplicate infections (performed twice for remdesivir, molnupiravir and nirmatrelvir and three times for camostat mesylate and E-64d). Half-maximal inhibition concentrations (IC50) were calculated using a non-linear regression model.