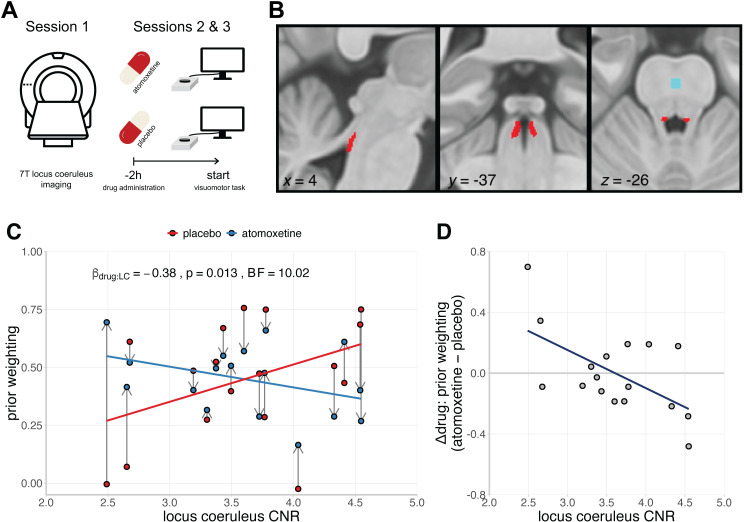
Fig 3. Baseline-dependent effects of noradrenaline on prior weighting.
A) Schematic overview of the noradrenergic drug study. The first session involved 7T MRI of the locus coeruleus, to estimate the mean contrast-to-noise ratio (CNR). The second and third sessions formed a double-blind randomised placebo-controlled crossover study, with 40 mg of oral atomoxetine of placebo. Two hours after drug administration, participants performed the visuomotor task that was designed to estimate prior weighting. B) Study-specific independent locus coeruleus atlas (red) and reference region in the central pons (blue). Image reused from O’Callaghan et al. [62] under a CC-BY 4.0 license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/). C) Estimates of prior weighting for participants with Parkinson’s disease, plotted as a function of their locus coeruleus CNR and the drug condition. Within-subject change in prior weighting from placebo to atomoxetine is indicated by the grey arrows. D) The relationship between the drug-induced change in prior weighting (atomoxetine minus placebo) and locus coeruleus CNR.