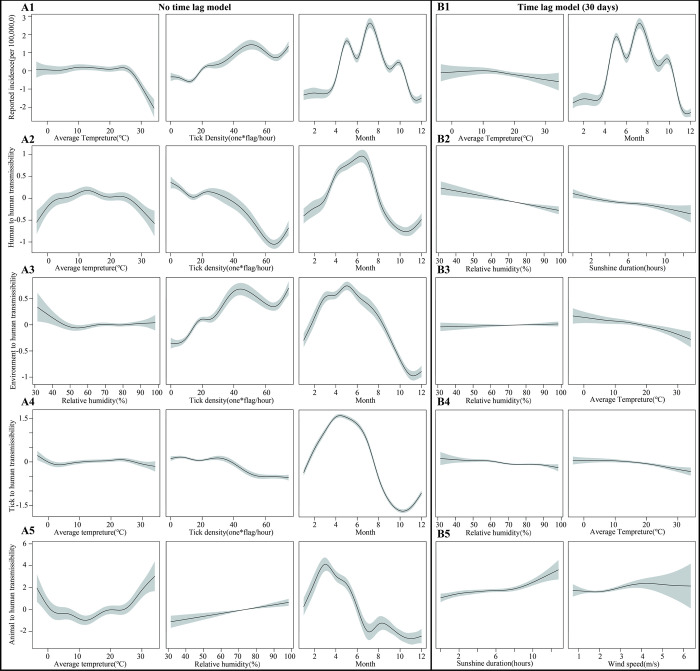
Fig 6. Non-linear relationship between SFTS incidence and different transmissibility with meteorological factors and tick density in Jiangsu Province.
Part A: SFTS incidence and different infection coefficients with meteorological factors and tick density in no time lag GAM; A1: Plots of non-linear relationship with factors associated with reported incidence; A2: Plot of non-linear relationship with factors associated with the infection coefficient of human-to-human; A3: Plot of non-linear relationship with factors associated with the infection coefficient of environment-to-human; A4: Plot of non-linear relationship with factors associated with the infection coefficient of tick-to-human; A5: Plot of non-linear relationship with factors associated with the infection coefficient of animal-to-human. Part B: SFTS incidence and different infection coefficients with meteorological factors and tick density in time lag GAM; B1: Plots of non-linear relationship with factors associated with reported incidence; B2: Plot of non-linear relationship with factors associated with the infection coefficient of human-to-human; B3: Plot of non-linear relationship with factors associated with the infection coefficient of environment-to-human; B4: Plot of non-linear relationship with factors associated with the infection coefficient of tick-to-human; B5: Plot of non-linear relationship with factors associated with the infection coefficient of animal-to-human).