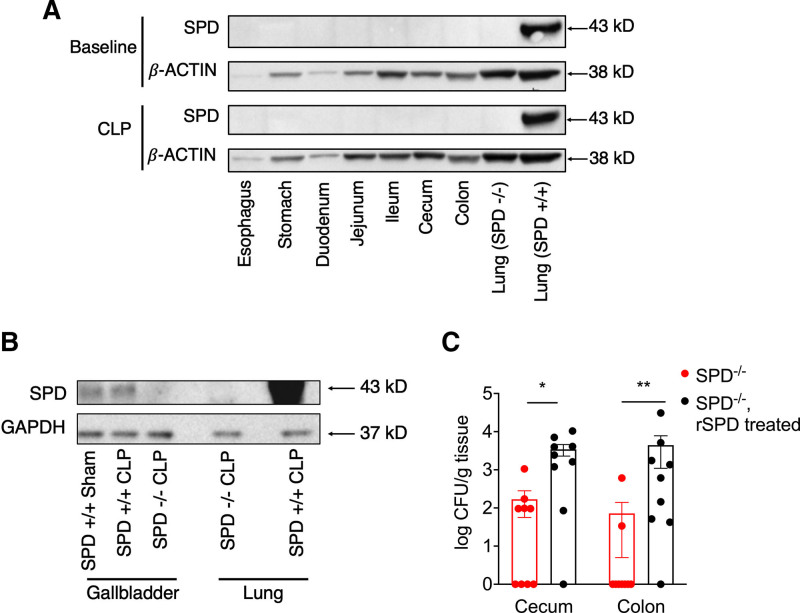
Figure 2.
Surfactant protein D (SPD) is synthesized by the gallbladder and promotes colonization of both the cecum and colon with Escherichia coli. A, SPD+/+ gut organs were harvested at baseline or post-cecal ligation and puncture (CLP) with Western blots performed for SPD or β-actin (loading control). Blots represent pooled samples, n = 2/group. Representative gel shown from three experiments. Lungs from SPD−/− and SPD+/+ mice were used as negative and positive controls, respectively. B, Gallbladder was isolated from SPD+/+ mice after CLP or sham surgery and from SPD−/− mice after CLP with Western blots performed for SPD or glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase antibody (GAPDH; loading control). Blots represent pooled samples, n = 5–7/group. Lungs from SPD−/− mice and SPD+/+ were used as negative and positive controls, respectively. C, SPD−/− mice (n = 9) were gavaged with recombinant surfactant protein D (rSPD), followed by gavage with green fluorescent protein (GFP)-labeled E. coli, and compared with SPD−/− mice gavaged only with GFP-labeled E. coli (n = 9). After 24 hr, cecum and colon were harvested. GFP-labeled E. coli were then detected by culture (Mann-Whitney *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01). CFU = colony forming units.