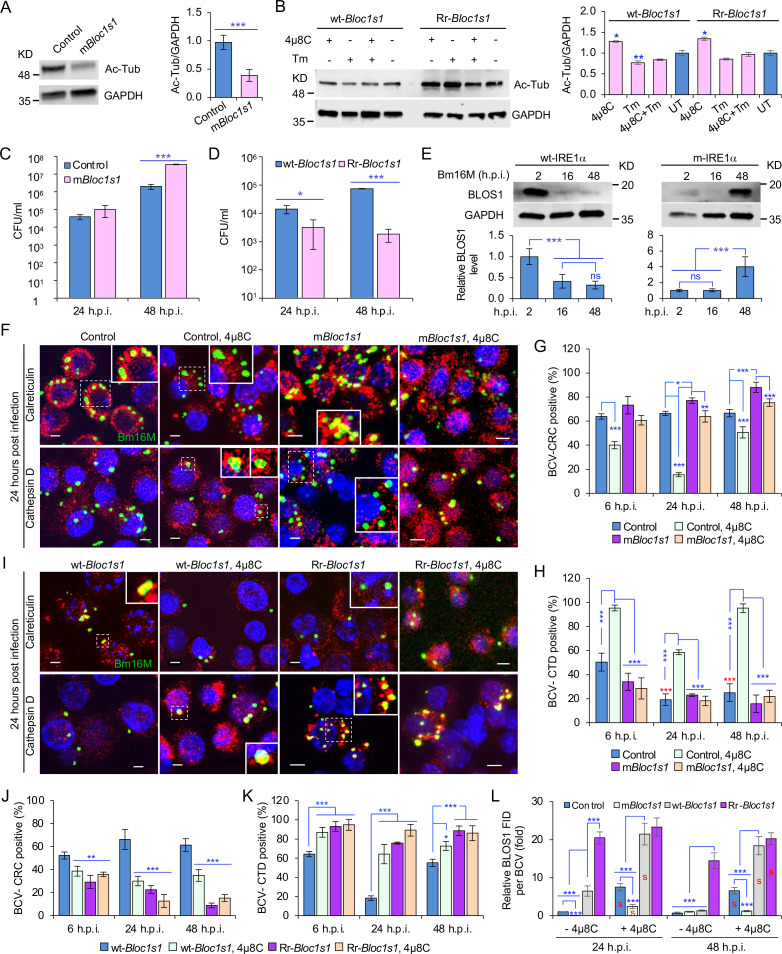
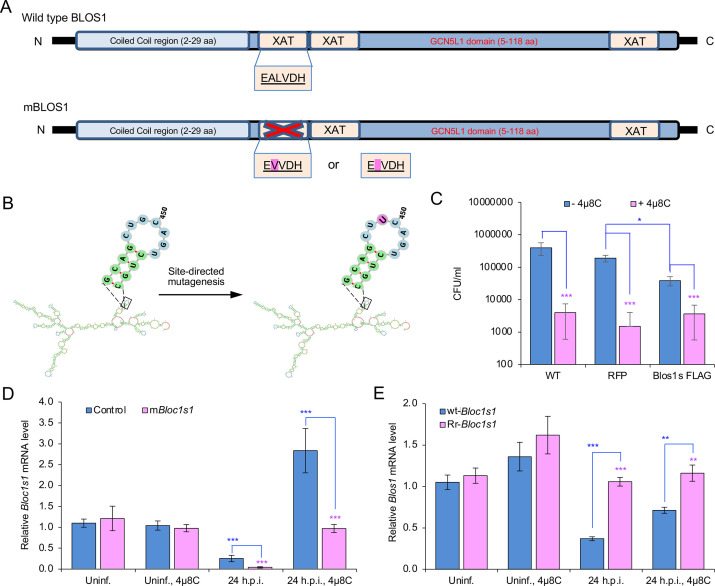
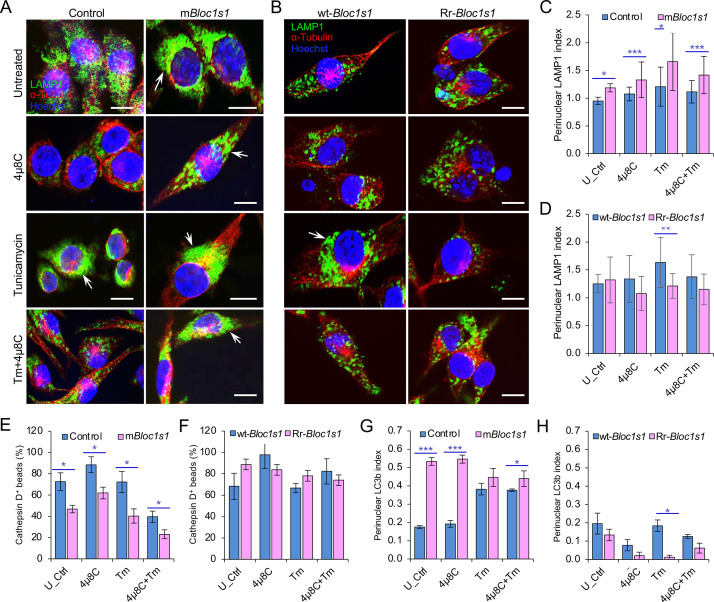
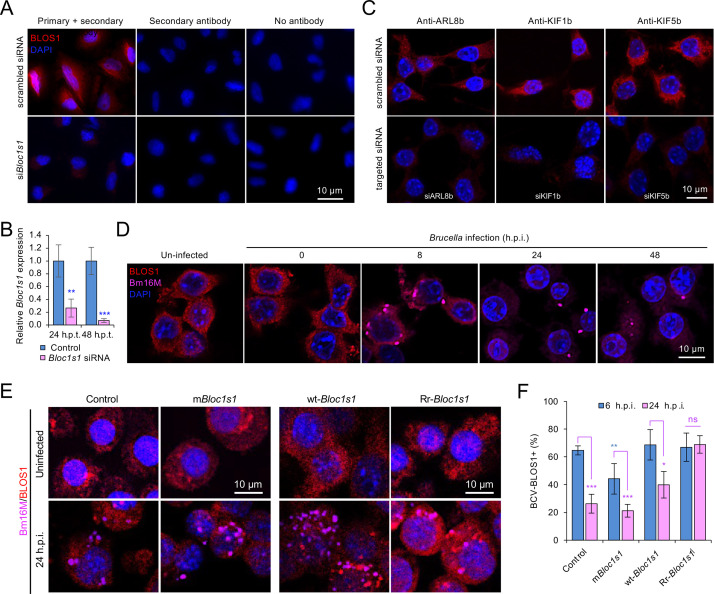
Figure 4. BLOS1 confers host cell susceptibility to Brucella infection and controls Brucella intracellular trafficking.
(A) Western blot analysis of α-tubulin acetylation (left) and quantification of α-tubulin acetylation level (right) in control containing Cas9 and a nonspecific gRNA and the nonfunctional Bloc1s1 mutant (mBloc1s1) in RAW 264.7 Cas9 cells. Ac-Tub: anti-acetylated antibody. (B) Western blot analysis of α-tubulin acetylation (left) and quantification of α-tubulin acetylation levels (right) in control (wt-Bloc1s1, overexpressing WT Bloc1s1) cells and cells that express the RIDD-resistant Bloc1s1 variant (Rr-Bloc1s1) treated or untreated with 4μ8C (50 μM), Tm (5 μg/ml), or both for 4 hr. CFU assays for Bm16M infection of RAW264.7 cells in which Bloc1s1 is nonfunctional (C), RIDD resistant (D) at the indicated h.p.i. (E) BLOS1 degradation assay during Brucella infection (upper panel) and quantification of the relative BLOS1 expression level (compared to the level of the loading control GAPDH) (lower panel) at the indicated h.p.i. ns: no significance. Colocalization of BCV with calreticulin (CRC) or cathepsin D (CTD) (F) and quantification of BCV-CRC+ (G) or BCV-CTD+ (H) in control and mBloc1s1 cells treated with or without 4μ8C (50 μM) at the indicated h.p.i. Red asterisks: significance (p < 0.001) compared to control cells at 6 h.p.i. Colocalization of BCV with CRC or CTD (I) and quantification of BCV-CRC+ (J) or BCV-CTD+ (K) in the wt-Bloc1s1 and Rr-Bloc1s1 cells treated with or without 4μ8C (50 μM) at the indicated h.p.i. (L) Quantification of BLOS1 fluorescence integrated density (FID) per BCV in the mBloc1s1, Rr-Bloc1s1, or their corresponding control cells treated with or without 4μ8C (50 μM) at the indicated h.p.i. S: significance (p < 0.01) compared to that without 4μ8C treatment. Host cells were infected with or without Bm16M, and at the indicated h.p.i., the cells were harvested for immunoblotting assays or fixed and subjected to confocal immunofluorescence assays. Blots/images are representative of three independent experiments. Statistical data represent the mean ± standard error of mean (SEM) from three independent experiment. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001.